- •
We tested predictions of a model for non-optimal animal movement in modified landscapes.
- •
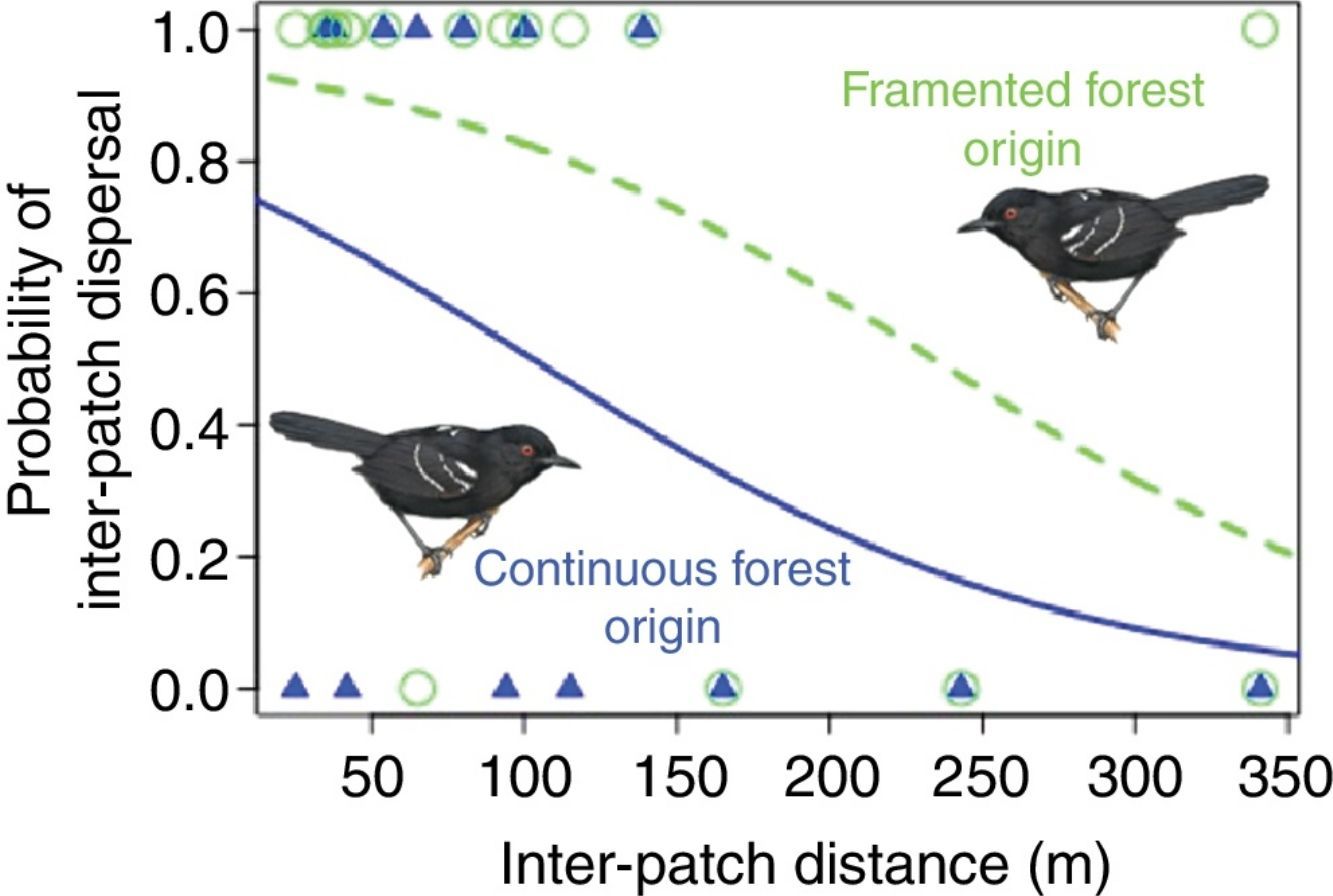
In fragmented landscapes dispersal success is lower for birds from continuous forests.
- •
Fragmented landscape birds are slow-explorers probably obtaining better information about the landscape.
- •
Dispersal success is higher for birds from fragmented landscapes.
- •
Gradual landscape changes should be favored to avoid non-optimal spatial behaviors.
- •
The predation risk was variable among the analyzed matrices (pasture, cornfields and Eucalyptus plantation)
- •
Differences between matrices can be perceived by individuals who change their behaviors in order to maximize benefits and minimize risk at each environment.
- •
The risk of predation can be reduced when the visual field facilitates the perception of fragments in the environment (pasture) or when the matrix offers resources and shelters (Eucalyptus).
- •
Tortuous movements can either mean lack of direction (i.e. visual obstruction, cornfield) or resource utilization or pauses to avoid predators (Eucalyptus).
- •
This study shows the importance of planning and managing matrices to reduce risks and favors landscape connectivity, especially around isolated native vegetation areas.
- •
Land changes can hinder landscape-level pollination through bee species loss.
- •
Bees were more diverse at functionally connected and highly heterogeneous landscapes.
- •
We propose non-linear effects of heterogeneity and functional connectivity on bees.
- •
Proper landscape-level bee pollination needs interspersed high quality environments.
- •
Burmese pythons are invasive to the Everglades and are expanding into more fragmented habitats.
- •
Movement behavior may impact how the landscape influences python populations in Florida.
- •
We used simulation modeling to investigate how behavior impacts population expansion.
- •
A behaviorally plastic boldness strategy best matched observed python expansion.
- •
Behavioral trade-offs and behavioral flexibility may influence population expansion.
- •
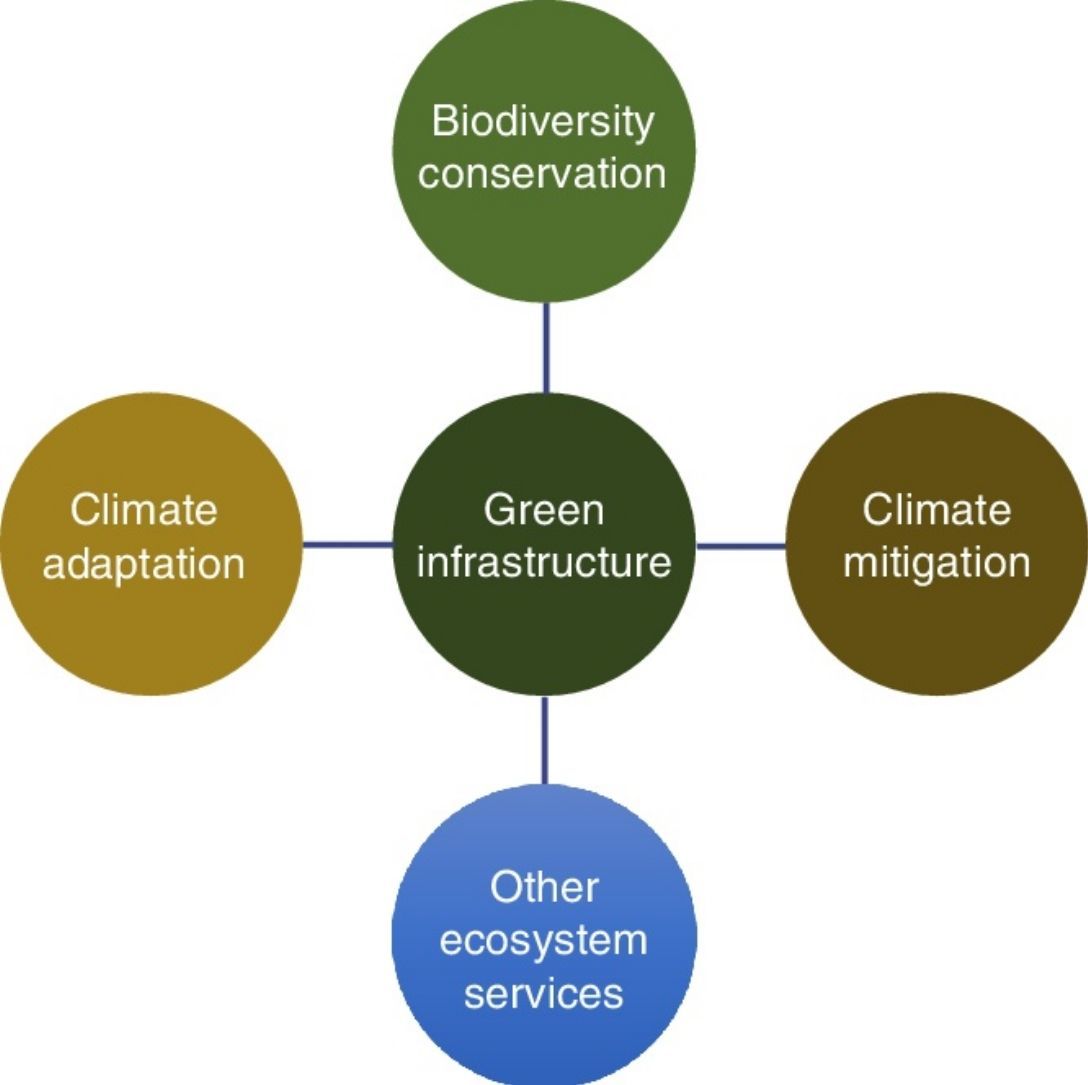
The concept of ecosystems as infrastructure is reviewed.
- •
The terms green, ecological, natural, and blue have been used in the literature.
- •
Green infrastructure is the most commonly used name.
- •
A more inclusive concept for green infrastructure is proposed.
- •
Design principles for green infrastructure at all spatial scales are suggested.
- •
Human activities increase the number of invasive species.
- •
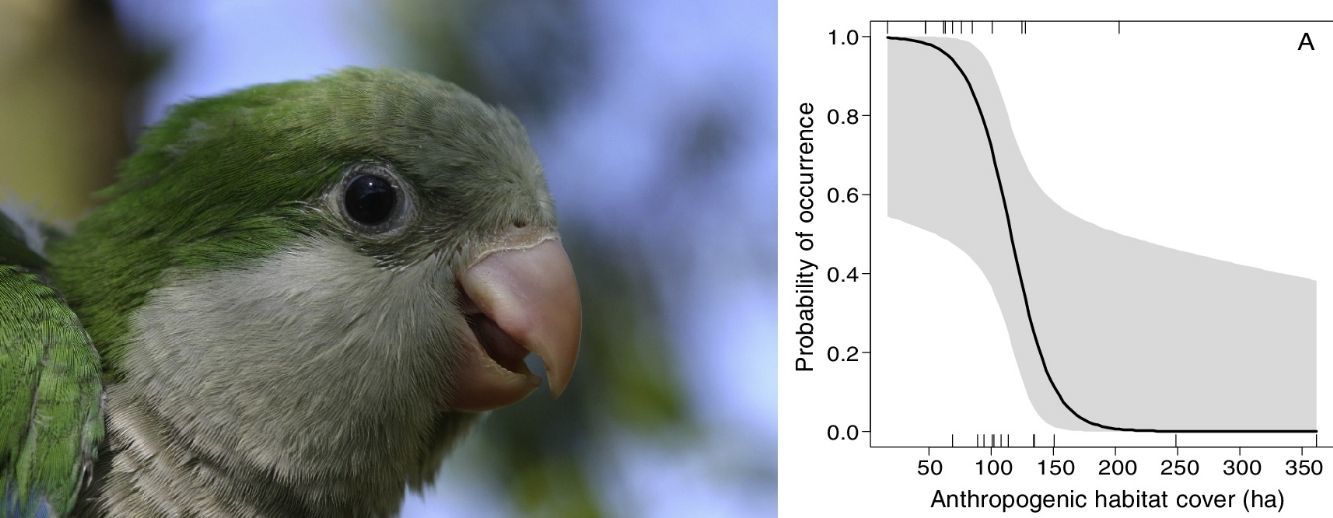
Landscape composition is related with invasive alien species occurrence.
- •
Landscape composition can be a useful landscape predictor of biological invasion.
- •
A landscape perspective may help to mitigate the impacts of invasive species on native biodiversity.
- •
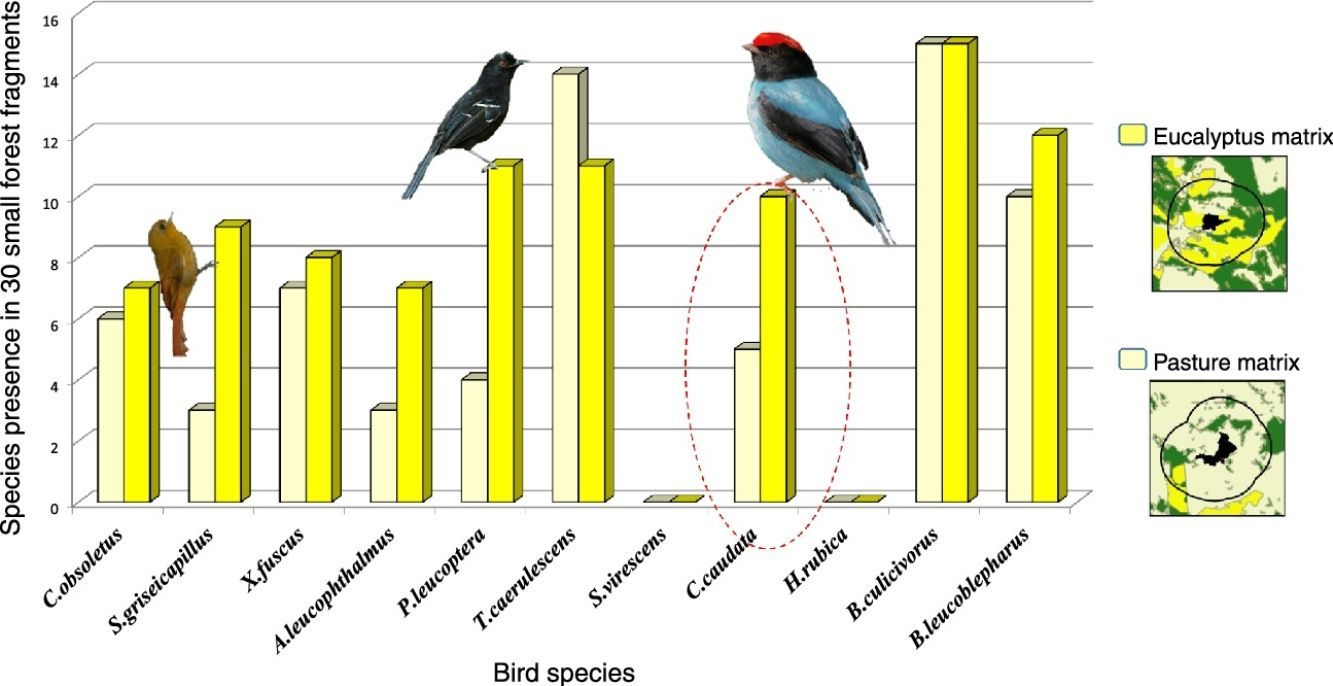
Small patches can increase landscape connectivity depending on the landscape context.
- •
The use of small patches by birds can be more influenced by matrix composition.
- •
Eucalyptus matrix favored a higher number of species in small patches.
- •
Almost half of Beaded lizards that encounter humans are victims of aversive hunting.
- •
Sightings increase in conserved areas whilst hunting may be explained by cultural dogmas.
- •
Dissemination of knowledge about Beaded lizards may greatly enhance their conservation.
- •
Habitat management and tolerance are essential steps in the conservation strategy.
- •
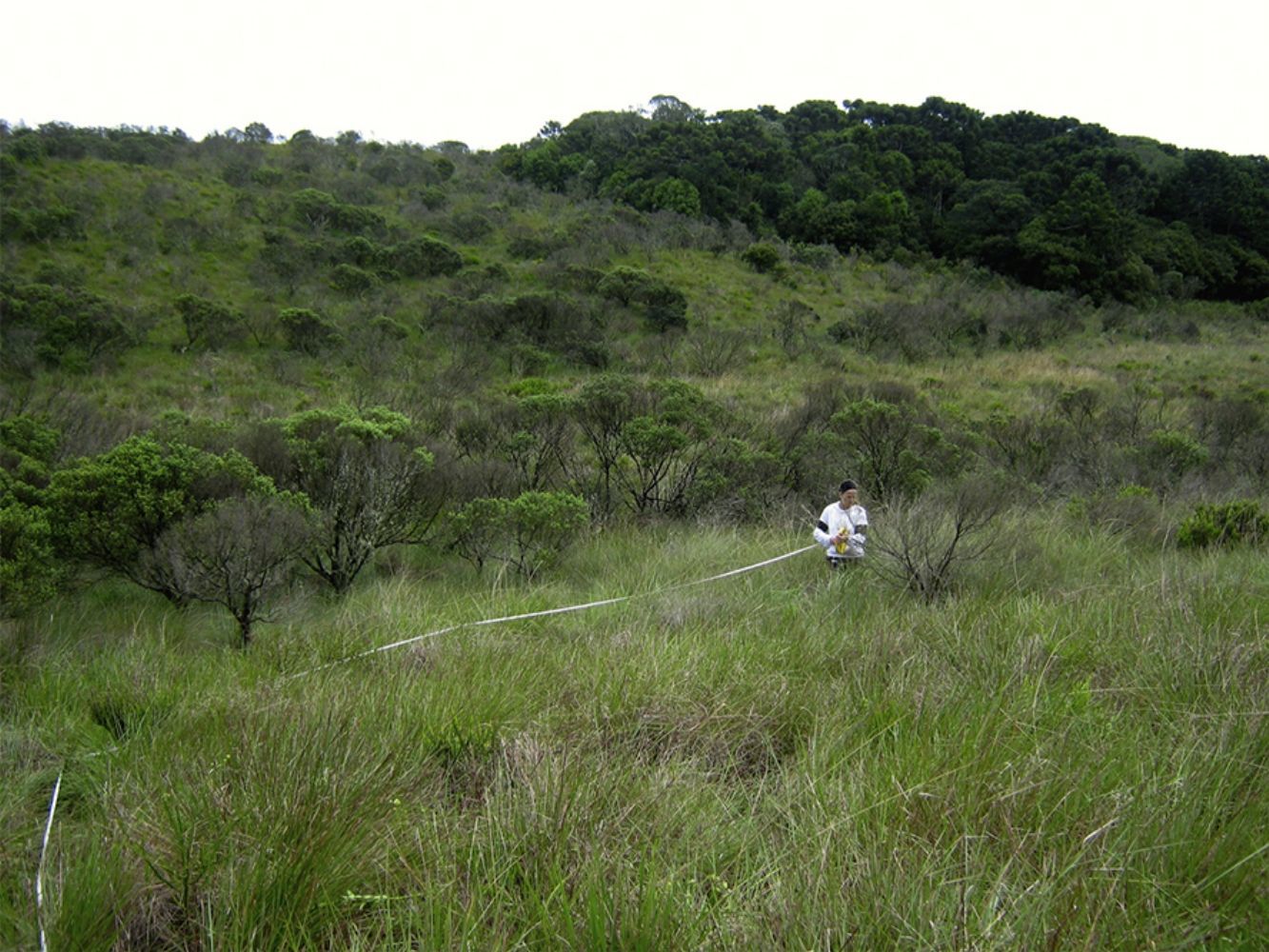
There are conservation concerns with shrub expansion due to lack of management.
- •
Baccharis uncinella encroachment affects grassland vegetation, reducing total plant richness.
- •
This study presents empirical data that contributes to conservation efforts of forest-grassland mosaics.
- •
Management practices that maintain forest-grassland mosaics are urgently needed.

- •
Spatial and temporal aggregation patterns of roadkills are recurrently used to mitigate road impacts.
- •
The aim of this study is to assess if hotspots/hot-moments remain in the same locations and periods over time and at different spatial and temporal scales.
- •
Hotspots and hot-moments occurred over time, but at large temporal and spatial scales.
- •
We suggest using longer road sections and longer time in order to minimize uncertainty.
- •
Costs and benefits using different spatial and temporal units to detect WVA are similar.
- •
Jaguar tourism contributes to economic and ecological sustainability of Pantanal.
- •
The Pantanal is the only brazilian biome that has policies for wildlife tourism.
- •
Government supervision applying tourism laws on Pantanal are limited.
- •
The tourism basically is self regulated by the guides and tourism operators.
- •
Pantanal has the potential to be an example to wildlife tourism development.




