Conservation actions should account for species natural history and behavior related to differences between sexes. However, most studies have not taken into consideration non-independence of observations from the same individual. We used data from camera-trap surveys undertaken over six consecutive years to investigate habitat use by jaguar (Panthera onca) in varzea seasonally flooded forest. We used hierarchical modeling to assess sex differences in occurrence probability related to environmental factors, while accounting for individual and spatial autocorrelation. Specifically, we tested whether male and female jaguars responded differently to habitat type and anthropogenic influence. Our results do not support previous conclusions related to differences between sexes and indicate that, in the studied area, jaguars are habitat generalists, exploring all environments with similar probability during the low-water season. Human settlements also apparently have little effect on habitat use by jaguars in this area. The lack of avoidance of settlements might be due to the low levels of anthropogenic pressure in the area, which adds support to the effectiveness of sustainable-development reserves. The difference between our results and previous studies may be due to the fact that we took into account individual differences, or may be related to the unique environmental characteristics of the varzea of Mamirauá Sustainable Development Reserve in Central Amazonia.
Habitat use has an important role in determining the distribution of organisms (Jonzén, 2008) and allows comprehension of factors affecting individual choice (Morrison et al., 2006). Vegetation structure is frequently assumed to be the main factor determining where and how species use resources (Block and Brennan, 1993). However, habitat implies more than vegetation, it is the sum of the specific resources that are needed by organisms and the way an animal uses physical and biological components in a place (Hall et al., 1997). Many species have been found to use habitat according to prey availability and to other environmental and anthropogenic factors (Rich et al., 2017).
Habitat requirements are not fixed. Carnivores may adjust behavioral and ecological strategies to different environmental conditions (Svoboda et al., 2019) and human-modified landscapes (Evans et al., 2019). Therefore, understanding the flexibility in carnivore habitat use is critical to better plan conservation actions and policies (Jędrzejewski et al., 2017).
Most carnivore habitat-use studies do not consider sex differences and tend to draw conclusions based on individuals of the most frequently observed sex, usually males (Gantchoff et al., 2019). Female carnivores often move less and have smaller home ranges than males (Gantchoff et al., 2019), and consequently tend to have a lower probability of detection that leads to fewer sightings (Sollmann et al., 2011).
Males and females may also show differences in the use of vegetation associations (Little et al., 2018). In general, males tend to be more tolerant to human disturbance, (Gantchoff et al., 2019), although some studies found that females are more likely to be found near human settlements (Bar-Ziv et al., 2022) and this behavior can lead to higher mortality rates due to conflict with people (Ramalho, 2012). However, the preponderance of conclusions related to sexual differences in habitat use of carnivores are based on studies with few individuals, low sampling effort and analyses that did not consider non-independence of observations of the same individual.
The jaguar (Panthera onca) is the largest felid in the Neotropics and its distribution includes many biomes, different types of vegetation associations and levels of human pressure (Morato et al., 2016). Jaguars are thought to show great plasticity and have a broad geographical distribution (De La Torre et al., 2018). Although jaguars display different patterns of resource selection across their geographic range, they often exhibit preference for high forest cover and areas close to watercourses (Sunquist and Sunquist, 2014). Moreover, human presence is likely to have a strong influence on resource-selection patterns and space use by jaguars (Morato et al., 2016). At local scales, there is variation in habitat use by jaguars, and individuals seem to select landscape features according to their availability (Morato et al., 2018). However, several studies concluded that individuals of different sexes respond differently to the environment; females tend to use dense cover forest and avoid human presence (Conde et al., 2010).
The Amazon forest holds the largest population of jaguars (De La Torre et al., 2018) and it is a crucial area for the long-term conservation of the species (Jędrzejewski et al., 2018), but little is known about the ecology and behavior of the jaguar in Amazonian flooded forests. The seasonally flooded forests inundated by sediment-laden rivers, known as varzeas, occupy about 3% of the Amazon basin (Ayres, 1993) and due to the seasonal flood pulse, local biological processes are highly dynamic (Junk et al., 1989). The Mamirauá Sustainable Development Reserve (MSDR) is a conservation unit that encompasses an area of varzea forest with traditional human occupants whose way of life is based on sustainable natural-resource exploitation (Queiroz, 2005). Jaguars in MSDR are known to display vertical migration in floodplain forests during the wet season, and adopt an arboreal and semiaquatic lifestyle during the entire flooded period; a unique behavior for a large terrestrial top predator (Ramalho et al., 2021). MSDR has one of the highest jaguar densities reported (Ramalho, 2012), a low human population density and highly productive environment (Junk, 1997), so jaguar behavior is likely to be different there even in the dry season.
Previous studies in MSDR, conducted during the low-water season, evaluated differential use of varzea habitats by jaguars and found a preference for aquatic/terrestrial transition zones (e.g., Alvarenga et al., 2018). However, none of earlier studies considered differences between individuals, sexes or tested the effect of human presence. In this study, we investigated habitat use by jaguar based on camera-trap surveys undertaken over six consecutive years in MSDR. We investigated jaguar habitat use in relation to vegetation structure, water availability and distance to human settlements. The first months of parental care of jaguars coincide with the dry season, probably increasing the probability of cub survival until the next flood season (Ramalho et al., 2021). To maximize the time their cubs have access to a dry landscape, we predicted that females would show a preference for high varzea, the highest area and the last to flood, and would stay at greater distances from water than males. Also, assuming that males are more tolerant of human presence, we hypothesized that males would be indifferent to human presence, whereas the probability of occurrence of females would be greater in areas further from human settlements.
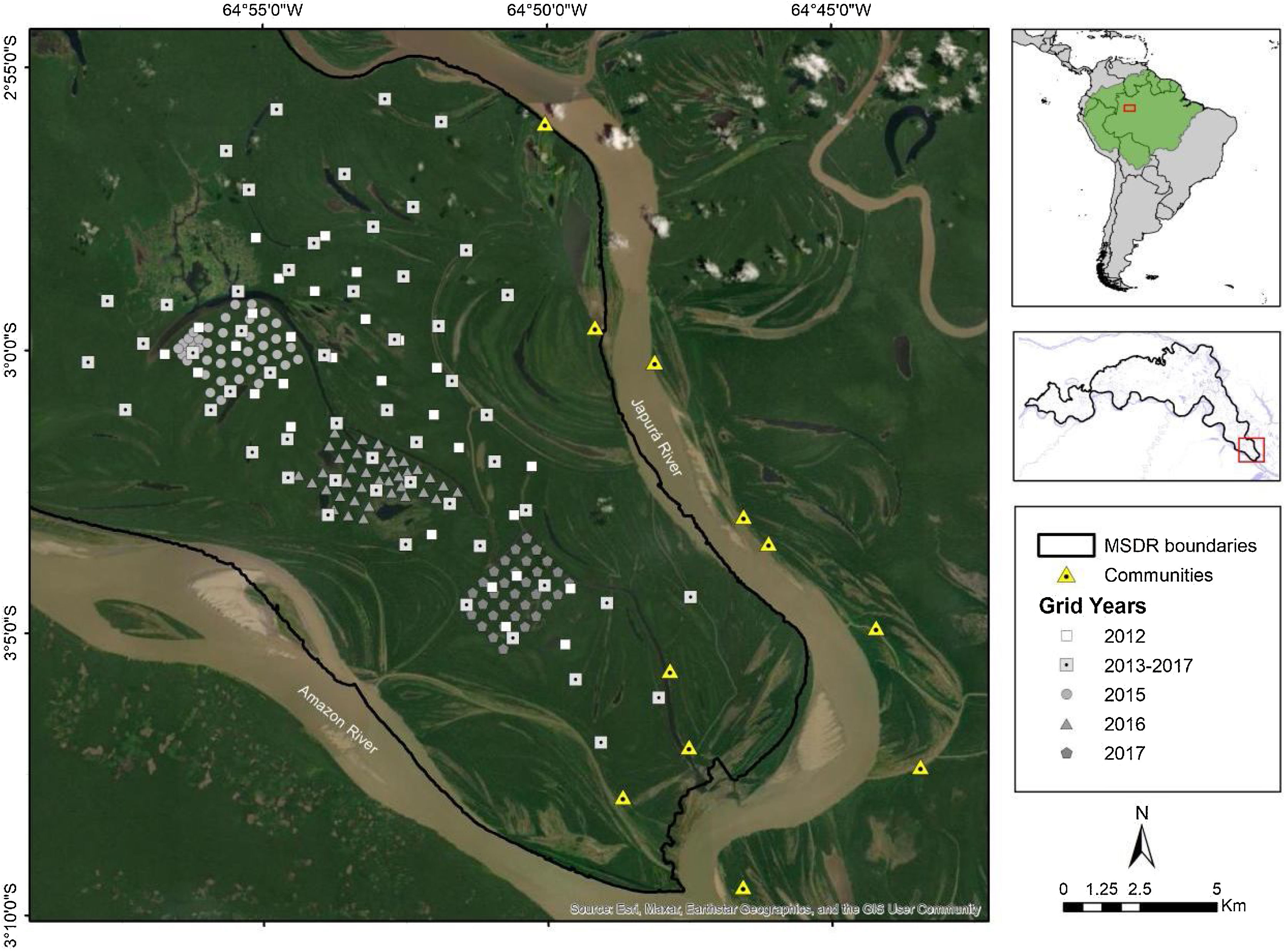
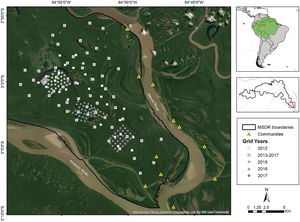
Materials and methodsStudy areaWe conducted the study in Mamirauá Sustainable Development Reserve (MSDR), located in Central Amazonia, Amazonas State, Brazil (1°49' to 3°09' S, 64°45' to 67°23' W). MSDR is delimited by the Amazon and Japurá Rivers (Fig. 1). The reserve encompasses 1,124,000 ha and represents the largest Brazilian protected area dedicated to varzea conservation (Queiroz, 2005). MSDR is flooded annually by nutrient-rich sediment-laden rivers for up to 175 days with an average annual vertical water fluctuation of >10 m (Ferreira-Ferreira et al., 2015).
The high-water season usually starts in May and runs until mid-July, usually with a peak in June, and water recedes from mid–July to September. The low-water season normally occurs between September and November, with lowest water levels recorded in October. The river level usually rises from the end of November to the beginning of May (Ramalho et al., 2009). Due to the difference in level and duration of flooding, the MSDR has three main vegetation types within the varzea landscape (Ayres, 1993). High varzea represents the terrain with highest elevation that is flooded for approximately four months per year by a water column that can reach up to 2.5 m. Low varzea covers most of the reserve, and occurs in intermediate terrain elevation with a generally open understory that can be flooded for up to six months per year by a water column of up to 5 m. Chavascal covers a smaller proportion of the MSDR forests. It is a swampy environment with lower vegetation and a dense understory, which can be flooded for up to eight months a year by a water column of seven meters or more (Ayres, 1993). Most of the variation in vegetation density is related to vegetation type and it is not possible to distinguish the effects of these two variables with the data available (Ayres, 1993; Ferreira-ferreira et al., 2015).
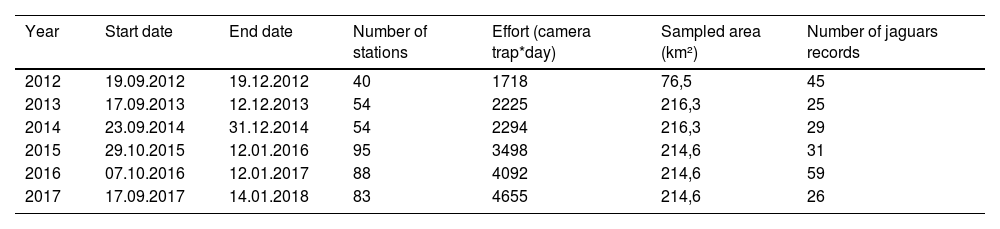
Camera trappingThe camera-trap sampling was originally designed to estimate the density of jaguars in the MSDR. The data were collected annually in the non-flooded period from September to January between 2012 and 2017 (Table 1). During the low-water season we set up camera-trap stations on a main standing grid with a total of 54 camera-trap stations that were repeated between 2013 and 2017, covering a total area of approximately 215 km2 (Minimum Convex Polygon). In 2012, data were also collected at 40 camera-trap stations covering a total area of 76 km2. From 2015 to 2017, we used a smaller grid inside the main grid, added to estimate the density of margays (area of approximately 6 km2). Each year, the smaller grid was locatd in a different portion of the main grid (Fig. 1; see Supplementary data for survey design details).
Summary of sampling effort per year for camera-trap monitoring in MSDR.
| Year | Start date | End date | Number of stations | Effort (camera trap*day) | Sampled area (km²) | Number of jaguars records |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2012 | 19.09.2012 | 19.12.2012 | 40 | 1718 | 76,5 | 45 |
| 2013 | 17.09.2013 | 12.12.2013 | 54 | 2225 | 216,3 | 25 |
| 2014 | 23.09.2014 | 31.12.2014 | 54 | 2294 | 216,3 | 29 |
| 2015 | 29.10.2015 | 12.01.2016 | 95 | 3498 | 214,6 | 31 |
| 2016 | 07.10.2016 | 12.01.2017 | 88 | 4092 | 214,6 | 59 |
| 2017 | 17.09.2017 | 14.01.2018 | 83 | 4655 | 214,6 | 26 |
To evaluate the influence of environmental variables on differences in habitat use between sexes, we recorded at each camera-trap station the main vegetation types following the classification of Ayres (1993). The three vegetation types were not similarly represented since every station were chosen randomly (see Supplementary data for predictor variables details). We also estimated minimum Euclidean distances between the nearest permanent water body for each station (see Supplementary data for predictor variables details). For this we used the shapefile of the hydrology of MSDR, which represents perennial water surfaces such as rivers, channels and lakes that do not dry out even in the driest period (Ferreira-Ferreira et al., 2015). As an indicator of possible human disturbance, we used the minimum Euclidean distance between each station and the nearest human settlement. The surrounding area has low human density, with a total of 235 residents (Sistema de Monitoramento Demográfico e Econômico - SIMDE/IDSM, 2019). All spatial measures were made using version 3.4 of the QGIS program (QGIS Development Team, 2019), with 30-m resolution layers.
Individual identity and sexJaguars were identified from their individual natural spot patterns and sex was attributed based only on their primary sexual traits (presence or absence of testicles on the individual, see Figs. S1 and S2) in the photographs. To avoid pseudoreplication, only detections of the same individual at a given camera trap station at intervals greater than 24 h were considered independent. When different individuals were distinguished in the same photo, they were considered separate events. Detections which did not meet those criteria or those in which sex could not be determined were excluded from analysis (n = 24).
AnalysesWe used hierarchical modeling to assess sex differences in the response of habitat use to environmental factors while accounting for individual- and site-level autocorrelation. We analyzed the data using generalized linear mixed-effects models (GLMM).
Our dependent variable was the individual occurrence and our sampling unit was presence or absence of a given individual at a given site. We first concatenated all individual occurrences (presence or absence) per single site throughout the sampling interval. The GLMM was based on observations of 38 individuals in 205 sites, and we assumed a zero-inflated binomial distribution with logit link to account for the very large proportion of zeros (97.5%). We used three predictor variables: vegetation type (coded as a categorical variable: High varzea, Low varzea, Chavascal), minimum distance to nearest watercourse and minimum distance to nearest human settlement. Sex (male or female) was included as a trait predictor, along with its pairwise interactions with each predictor to test whether any environmental and anthropogenic response depended on sex. Sampling effort (number of working days per station) was also included as a covariate to control for variation in effort among sites.
The hierarchical data structure potentially created autocorrelation among observations from the same individual and/or site. Accordingly, individual and site identity were used as random factors to account for such non-independence, which is equivalent to a split-plot design (individual x site) with missing combinations.
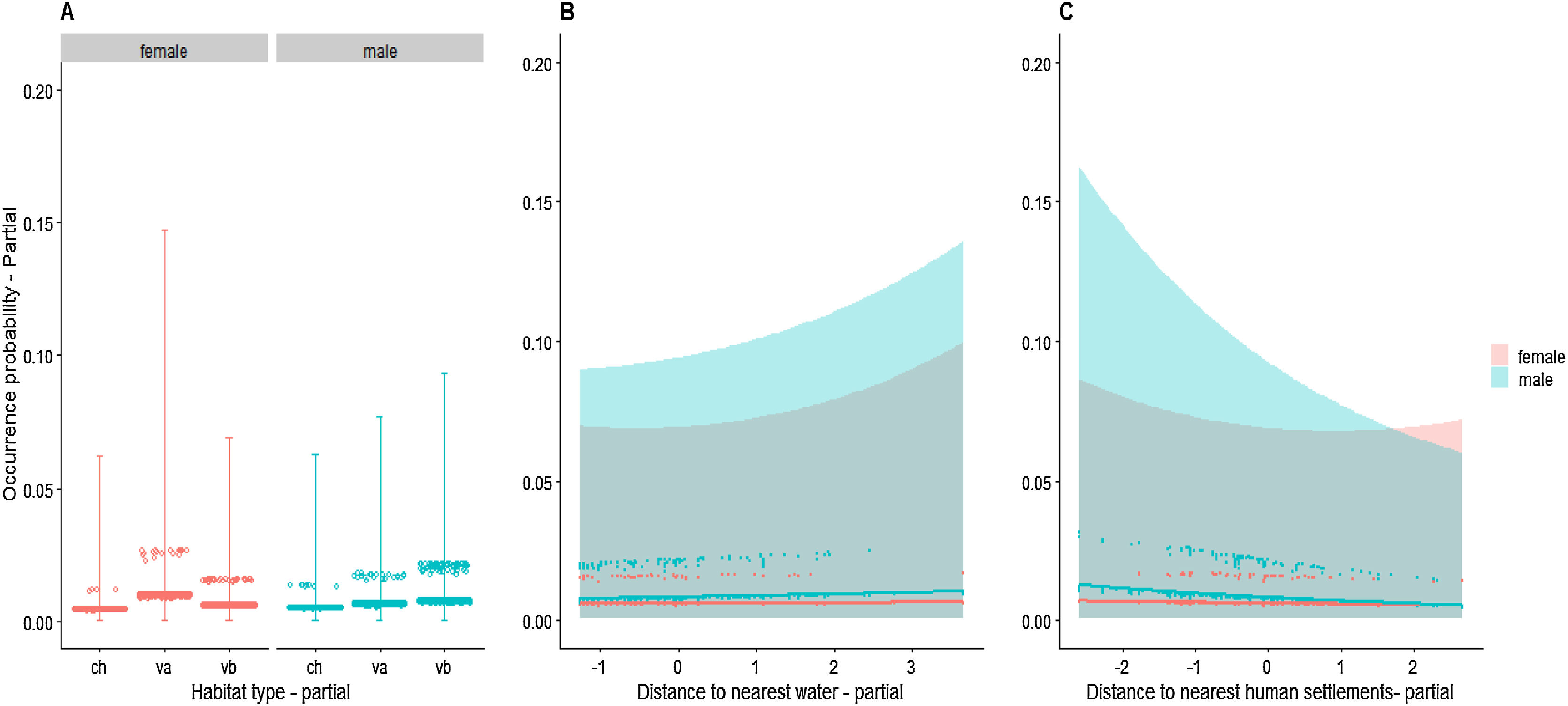
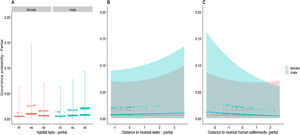
First, we built a model including all predictors, in which “site” was represented by a random intercept, and “individual” was represented by random intercept and slope. This allowed for random variation in individual responses to environmental and anthropogenic factors, beyond any sex effect (Jamil et al., 2013). However, this model did not converge to stable parameter estimates; possibly due to “testing on the boundary”, (i.e., variance of random slopes was so small that they could not be discriminated from zero). Therefore, we only considered random intercepts. Next, we checked for significant (P < 0.05) interactions between environmental and anthropogenic factors and sex. If interactions were not significant, they were excluded and the model was refit to test for independent effects. All the continuous predictors were scaled to zero mean and unit variance to avoid convergence problems during parameter estimation. To visualize the response of occurrence probability to each tested interaction while controlling the remaining predictors, we used conditional plots (Breheny and Burchett, 2017).
We checked model residuals for spatial autocorrelation using Moran’s I (Fig. S3) with the function ‘spline.correlog’ from the package ‘ncf’ (Bjornstad and Cai, 2020). This function calculates the confidence interval for autocorrelation at different distances along the distance gradient; if this interval includes zero there is no evidence of non-zero autocorrelation. Nearby values of variables were smaller than expected at random. Sensitivity analysis showed that the results were little affected by the sample size (see Supplementary data in analisys details). All models were fit using restricted maximum likelihood, as implemented in R 4.2.1 (R Development Core Team, 2021) by the function ‘glmmTMB’ from the self-title package (Brooks et al., 2017) and package ‘Car’ (Fox et al., 2018).
ResultsPredictor variablesThe three vegetation types had the following coverage proportions during all years of study: Chavascal (14%), Low varzea (65%) and High varzea (21%). The minimum estimated distances (in meters) between the nearest permanent water body and each camera-trap station was 15 m and maximum was 1392 m (mean 332 m). The average distance between each station and the nearest human settlement was 8388 m (min. 925 m – max. 16574 m). This result is in accordance with the sinple graph (Figs. S4 and S5, see in Supplementary data) showing that the frequency of encounters of jaguars was largely proportional to the frequency camera traps at given distance for both sexes.
Individual identity and sexFrom the six consecutive years of camera-trap surveys in MSDR we obtained 153 independent records from identified jaguars, 100 records of males and 53 of females. We were also able to identify 38 jaguar individuals, 23 males and 15 females, giving an observed sex ratio of 1.5:1 (m: f).
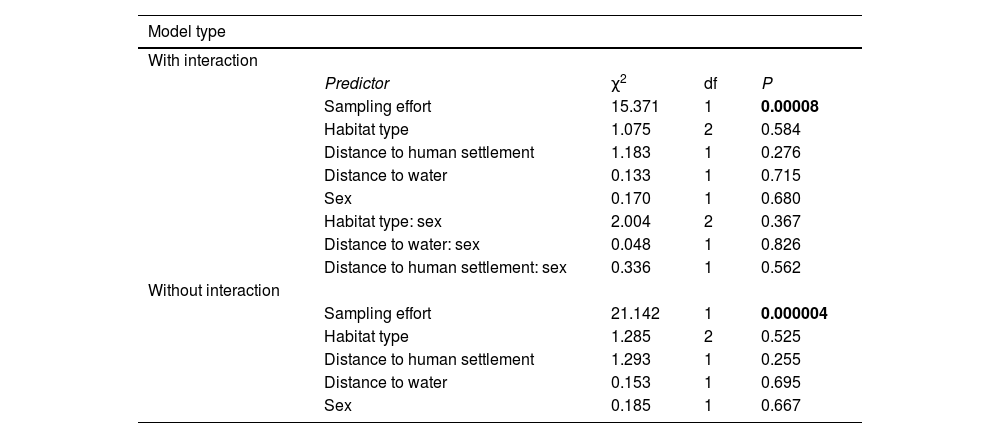
AnalysesWe did not detect differences in probability of occurrence between males and females with respect to any environmental or anthropogenic variables (Table 2, Fig. 2). Sampling effort was the only variable with a significant effect. As expected, the longer the sampling time, the greater the chance of detecting a jaguar by a camera trap.
Results of a Generalized Linear Mixed Model (GLMM) of jaguar occurrence in Mamirauá Sustainable Development Reserve, testing for interactions between sex and environmental/anthropogenic variables (n = 7790). Jaguar occurrence-probability was modeled assuming a logit link function and zero-inflated binomial errors, including site (n = 205) and individual (n = 38) as random factors. χ², chi-squared statistic; df, degrees of freedom of model term; P, probability under the null hypothesis that the true model term is zero. Bold numbers indicate significant model terms (P < 0.05).
| Model type | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| With interaction | ||||
| Predictor | χ2 | df | P | |
| Sampling effort | 15.371 | 1 | 0.00008 | |
| Habitat type | 1.075 | 2 | 0.584 | |
| Distance to human settlement | 1.183 | 1 | 0.276 | |
| Distance to water | 0.133 | 1 | 0.715 | |
| Sex | 0.170 | 1 | 0.680 | |
| Habitat type: sex | 2.004 | 2 | 0.367 | |
| Distance to water: sex | 0.048 | 1 | 0.826 | |
| Distance to human settlement: sex | 0.336 | 1 | 0.562 | |
| Without interaction | ||||
| Sampling effort | 21.142 | 1 | 0.000004 | |
| Habitat type | 1.285 | 2 | 0.525 | |
| Distance to human settlement | 1.293 | 1 | 0.255 | |
| Distance to water | 0.153 | 1 | 0.695 | |
| Sex | 0.185 | 1 | 0.667 |
Conditional plots of jaguar occurrence probability in relation to (A) habitat × sex interaction, (B) distance to watercourse × sex interaction, and (C) distance to human settlement × sex interaction. Each point (n = 7790) represents a record of an individual (n = 38) in a given site (n = 205). Grey areas indicate 95% confidence intervals. Plots show focal relationships after accounting for remaining predictors. ch: chavascal; va: high varzea; vb: low varzea.
Even when we removed interactions between sex and other variables and tested only for independent effects, nothing other than sampling effort had detectable influence on occurrence-record probability (Table 2, Fig. S6, see in Supplementary data). All models, with and without interaction terms, did not show significant spatial structure in the residuals (Fig. S3).
DiscussionOur results indicate that, in the varzea of central Amazonia, jaguar habitat use was unrelated to vegetation type, regardless of sex. Jaguars used High varzea, Low varzea and Chavascal in our study area with similar probability to their availability. Contrasting with our findings, preliminary studies in MSDR, indicated that jaguars were most frequently found in the lowest areas in the reserve (e.g., Alvarenga et al., 2018). However, those studies used a different analytical approach, a smaller temporal scale, and did not consider spatial or individual autocorrelation. Studies conducted in different locations have reported that females may select habitats with higher quality, that give them better access to shelter and prey (Gese et al., 2018), and a preference of females for primary forest, whereas male jaguars are more likely to use open areas, such as pasture and agricultural areas (Conde et al., 2010). However, recent studies involving a greater number of telemetered individuals from different biomes, including a few individuals from MSDR, did not find differences of occupancy probabilities between sexes in relation to environmental variables, though they found a positive correlation between occurrence and forest cover in general (Morato et al., 2018; Thompson et al., 2021). Although those studies investigated a different scale, the results support our analysis, which found that male and female jaguars exhibit similar habitat-use patterns in the same area. MSDR vegetation types form a mosaic throughout landscape. Therefore, as jaguar home ranges are large enough to include all the vegetation types, there is no evidence of one vegetation type being used preferentially in low water season.
Although a significant portions of the jaguar’s diet may be comprised of aquatic and semiaquatic species in seasonally flooded ecosystems (Da Silveira et al., 2010), suggesting that there might be pressure to select areas close to water, we found no evidence of this association in either sex. In general, jaguar occurrence is usually higher near water bodies (Sunquist and Sunquist, 2014), but it is not clear whether this relationship varies between sexes. Some studies have concluded that males select locations closer to water sources than females (Gese et al., 2018), but others have reported that females occur closer to water (Foster et al., 2010). However, in places where large and permanent water sources are available throughout the year, distance to water may have no impact on jaguar occurrence (Ávila-Nájera et al., 2019). MSDR sustains high caiman densities (Da Silveira et al., 2008), one of the main prey species of jaguar in this ecosystem (Ramalho, 2006). This associated with the fact that MSDR is a varzea island limited by two of the widest rivers in Amazonia and interspersed by numerous watercourses, suggests that proximity to water is not a good predictor of jaguar habitat use in this environment.
We did not find evidence of the influence of human disturbance or sex on jaguar distributions in the dry season. Although human presence has been found to be an important factor that negatively affects the occurrence and activity of jaguars in some studies, it does not seem to influence their occurrence where the disturbed environment is surrounded by dense vegetation cover (Ávila-Nájera et al., 2019), or inside protected areas with low human pressure (Mena et al., 2020), such as in our study site. Evidence of human activities is negatively correlated with the probability of jaguar occurrence most likely because it is correlated with density of hunters (Jędrzejewski et al., 2018), and prey and predator abundance decline with human access (Espinosa et al., 2018). Jaguars are also affected by roads (Cerqueira et al., 2021; see Road effects in supplementary data), but the Mamirauá area is essentially roadless. In a study conducted in MSDR, based on interviews with local people, the mortality rate for jaguars killed by hunters was almost twice as high for males than for females, which was attributed to differences in movement patterns between sexes (Ramalho, 2012), but this is close to the sex ratio detected by our camera traps (1.5:1). The lack of evidence of an effect of human disturbance on the distribution of jaguars in MSDR is probably because the density of people is low in all areas and hunting pressure on jaguar prey is relatively low. Also, the forest in the surroundings may favor jaguar habitat use (e.g., Cerqueira et al., 2021).
Jędrzejewski et al. (2017) suggested that jaguar populations appear to be less vulnerable to extirpation in humid and highly productive zones than in dry and unproductive areas. Jaguars apparently adjust their behavior according to the type of landscape conditions they are in, so that home-range size decreases with net primary productivity (Thompson et al., 2021). The MSDR soils (typical varzea) are nutrient rich, which results in high plant productivity ( Wittmann et al., 2004) that can support high densities of prey (e.g., Da Silveira et al., 2008) and predators (Ramalho, 2012). Since the quantity of food and shelter are high, jaguars might not need to be selective of a particular environment. Furthermore, the home ranges of jaguars cover relatively large areas (Morato et al., 2016) that encompass all vegetation types (Ferreira-Ferreira et al., 2015). Therefore, food resources in the varzea are probably not limiting for jaguars. The use of a given habitat relative to its availability varies in response to environmental conditions, leading to very different habitat-selection processes in different environments. Thus, in productive environments, habitat selection processes may not respond to habitat heterogeneity (Gaudry et al., 2018). Nevertheless, it will not be possible to confirm that the lack of selectivity by jaguars is unique to várzea habitat until similar studies, taking into account individual- and site-specific autocorrelation, are undertaken in other environments.
ConclusionsOur data set allowed us to consider individual variability induced by home-range location, which reinforces the conclusion that jaguars are habitat generalists in the varzea of MSDR during the non-flooded season. However, our results do not support conclusions related to differences between sexes in habitat use, water availability or avoidance of human settlements. The difference between this and previous studies may be due to taking into account individual diferences, or may be related to the unique environmental characteristics of the varzea of MSDR, a place with high productivity, periodic flooding associated with isolation by large rivers that limit the migration of even large mammals (Alvarenga et al., 2018), selecting populations morphologically and behaviorally adapted to these conditions in MSDR (Ramalho et al., 2021).
Amazonia plays a key role for long-term conservation of the jaguar and holds 50% of the species’ current range, which is the reason that it has long been considered the jaguar’s stronghold (Lorenzana et al., 2020). Varzea, despite being the Amazonian ecosystem with the highest human presence, is an important stronghold for jaguars and should be protected wherever possible. While most studies have shown that jaguars are positively associated with forest cover and water sources, and negatively related to human presence (Morato et al., 2018), our results suggest that, in MSDR, jaguars are habitat generalists, exploiting all environments with similar probability during the low water season. Human disturbance apparently has little effect on space use by jaguars in the MSDR, indicating that low-density human settlements in sustainable-development reserves can coexist with wildlife, including top predators. However, the increase in the density of settlements may lead to more intense conflict with humans. Protected areas play a key role in maintaining diversity and serve as final refuges for endangered species, such as the jaguar, throughout their distributions (Mena et al., 2020).
Conflict of interestThe authors declare no conflict of interest.
We are grateful to the many professionals, who aided us in the field surveys: Fernando Ferreira de Pinho, Almir Carvalho de Araújo, Lázaro Pinto dos Santos. We thank Anderson Saldanha Bueno and Raquel Fernandes de Araujo for help with spatial analysis. We thank Maíra Manzan for help with the graphical abstract. We are indebted to Fernando Ferreira Pinho for insightful criticisms of previous drafts of the manuscript. We thank the Mamirauá Sustainable Development Institute, the Betty and Gordon Moore Foundation, and CNPq (Brazilian Government Research Council) for the financial support. This study was financed in part by the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior - Brasil (CAPES) - Finance Code 001. WEM received a productivity grant from CNPq.