The critically endangered Brazilian Merganser Mergus octosetaceus is one of the rarest waterfowls in the world. Only three isolated populations remain in the Brazilian Cerrado, totaling less than 250 individuals. We evaluated the potential influence of small hydroelectric plants (SHPs) and Protected Areas (PAs) on the species’ conservation. We identified suitable areas by using recent presence records and environmental predictors, and overlapped it with the species dispersion zone and the SHP impact zone. Suitable areas for the species are limited to 4% of the geographic space (142,899km2). Within the dispersion zone, we found 36 planned SHPs, which can impact 4.1% of the suitable area and 17.2% of the suitable area inside PAs. Our results expose the critical situation of the Brazilian Merganser, with few isolated suitable areas, high potential impacts for the three known populations, and a high proportion of suitable areas out of PAs. We highlight the need of considering SHPs impacts on the Brazilian Merganser in environmental impact assessment studies to reduce them. Furthermore, we appointed areas for search of new populations, and emphasize how urgent the implementation of effective conservation actions aiming to protect the remaining suitable habitats for the Brazilian Merganser is.
The Brazilian Merganser Mergusoctosetaceus is an endemic South American waterfowl, inhabiting clear and rapid river courses sided by gallery forest of mountainous regions (Hughes et al., 2006). It is considered rare and threatened of extinction since the 1950s (Partridge, 1956) with no recent records (for the last 15 years) in Argentina, Paraguay, and southern Brazil (Collar et al., 1992; Hughes et al., 2006), places in which the species is likely extinct. Nowadays, the remaining populations are only found in three regions of Central Brazil: Serra da Canastra (Silveira and Bartmann, 2001; Ribeiro et al., 2018), Chapada dos Veadeiros (Bianchi et al., 2005), and Jalapão (Barbosa et al., 2015). The current population has less than 250 individuals and is decreasing (BirdLife International, 2019), setting the Brazilian Merganser as one of the most endangered bird species of America. It is considered critically endangered globally (BirdLife International, 2019) as well as in Brazil (MMA, 2014) and extinct or critically endangered in several Brazilian states (COPAM, 2010; SEMA, 2017; Paraná, 2018; São Paulo, 2018). It is classified within the criteria C2a (i) and C2a, meaning that its population is small, continuously declining and that no subpopulation has more than 50 individuals (Disconzi, 2012). The Brazilian Merganser National Action Plan (hereafter BMNAP), a Brazilian governmental initiative created to organize conservation actions for this endangered species proposed several actions to ensure the maintenance and recovery of populations in the wild. Recently, the Brazilian Merganser was also declared a Symbol of the Brazilian Waters (MMA, 2018) due to the combination of its highly threatened status and specific ecological requirements.
The Brazilian Merganser is a visual predator and requires clear water for fishing (Partridge, 1956; Hughes et al., 2006), thus river pollution and siltation due to human activity are some of the main threats for the species. The building of dams for energy production poses additional threats to the species (Yamashita and Valle, 1990, Hughes et al., 2006) by altering rivers’ traits, water quality, and the hydrological cycle (Bunn and Arthington, 2002). There is a growing interest of the Brazilian government to invest in small hydroelectric plants (SHP, capacity<30MW and dam surface area ≤3km2) in the last years as an alternative to conventional hydroelectric plants (Ferreira et al., 2016). Brazil already has 455 SHPs in operation and 1577 more are planned to be built in the coming years (ANEEL, 2020). In Cerrado, the unique biome where the Brazilian Merganser remains, 128 are already in operation and 625 are planned to be built.
Considering the current status and threats to the Brazilian Merganser and its conservation needs, this study aimed to identify the remaining suitable areas for this species that are currently protected by Brazilian Federal Laws (Brazil, 2000), as well as to quantify the amount of suitable area likely threatened by the construction of new SHPs. We used the Species Distribution Model (SDM) as a tool to identify suitable areas by recent presence records and environmental predictors. SDM was used as a tool in a Participatory Modelling Process (PMP), in which the participants of the BMNAP workshop were engaged to co-produce and to select the best model explaining the species distribution (Ferraz et al., 2020). SDM has been successfully used for spatial conservation prioritization (Morato et al., 2014; Paviolo et al., 2016), for guiding the search for new populations (Rhoden et al., 2017), and for forecasting scenarios under climate change (Vale et al., 2018) and deforestation (Rocha et al., 2020). Moreover, SDMs have been frequently used as part of other National Action Plans in Brazil and in many worldwide conservation workshops for endangered species as a tool that successfully guides decisions towards species conservation (Ferraz et al., 2020).
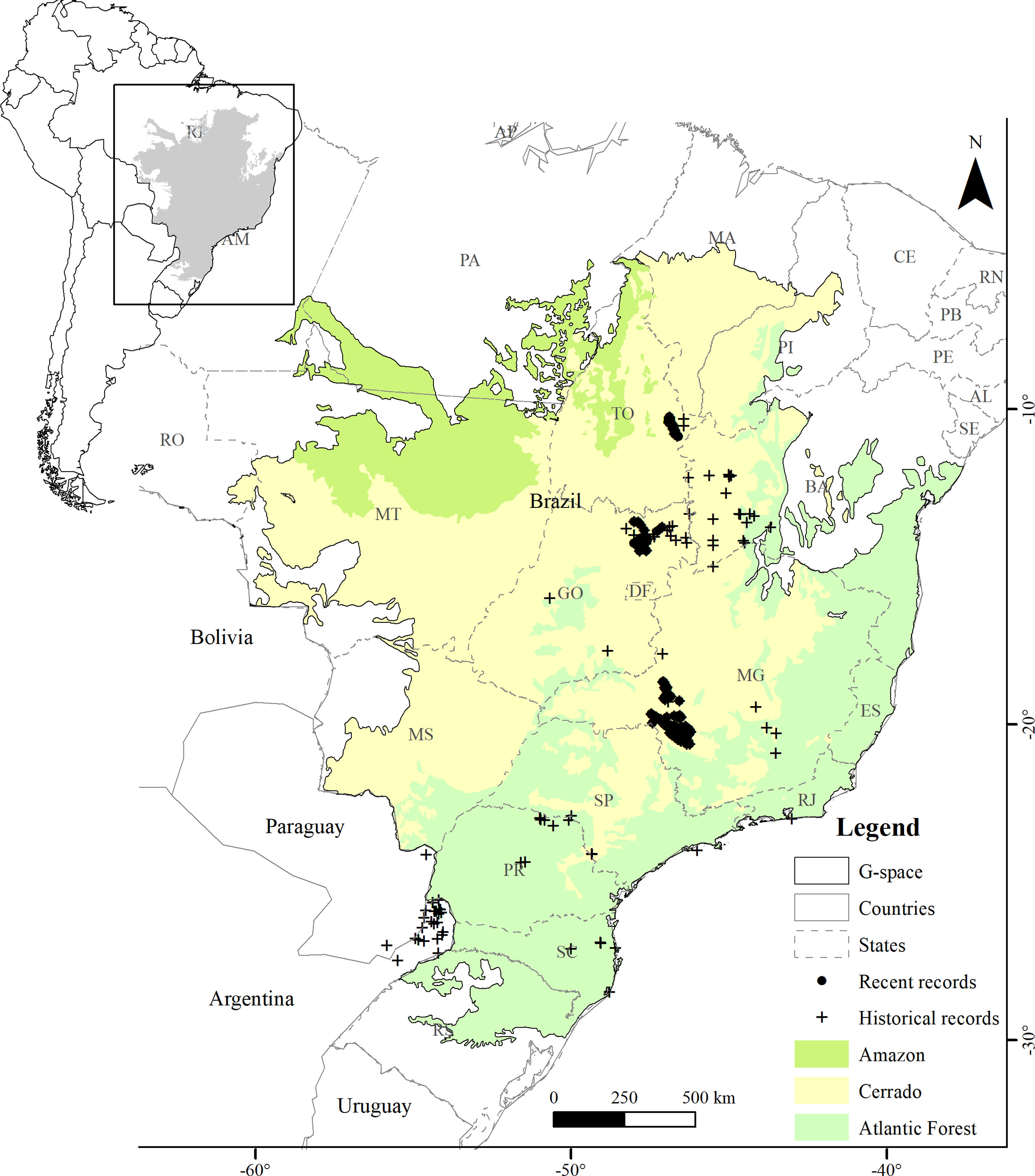
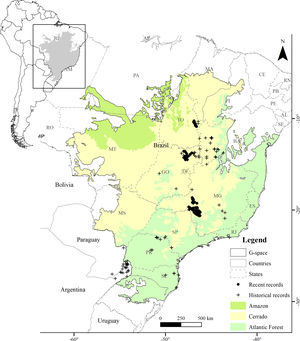
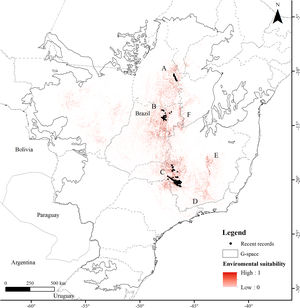
MethodsStudy areaWe defined the geographic space to model the distribution of the Brazilian Merganser based on the map of world ecoregions (Olson et al., 2001). We included all ecoregions with historical and recent records, plus adjacent ecoregions with ecological similarity: Cerrado and Campos Rupestres montane savanna in the Cerrado, Araucaria moist forest, Bahia interior forests, Bahia coastal forests, Serra do Mar coastal forests, Atlantic dry forests and Alto Paraná Atlantic forest in the Atlantic Forest, and Mato Grosso seasonal forests in the Amazon (Fig. 1). We limited the geographic space to the Brazilian territory (3,477,191km2), as the species has not been recorded in Argentina and Paraguay since 2002 and 1984, respectively (Lesterhuis et al., 2004; Hughes et al., 2006), even after recent efforts (Esquivel et al., 2019; Anfuso et al., 2020).
The main current habitat of the Brazilian Merganser is the largest Neotropical savanna (i.e. Cerrado), located in the center of South America, which harbors the remaining population. It is composed by a mosaic of different vegetation physiognomies varying from grasslands (campo limpo) to savannas (typical cerrado sensu stricto) and cerrado woodlands (cerradão/dense forest). Projections for the coming decades indicate that the largest increase in agricultural production in the country will occur in this region (Laurance et al., 2014; Klink and Machado, 2005), stimulated and supported by the new Forestry Code (2012) that allows for increased legal deforestation in the Cerrado (Soares-Filho et al., 2014). Between 42% and 46% of the Cerrado has already been converted to anthropogenic land use cover (Strassburg et al., 2017; Projeto MapBiomas, 2019), and projections estimate a loss of 31–34% of the remaining natural cover by 2050 (Strassburg et al., 2017). Cerrado is a Neotropical biodiversity hotspot (Mittermeier et al., 2011), and only 2.72% of its area is under strict protection (CNUC, 2020).
The Atlantic Forest is located mostly across the Brazilian eastern coast, mainly composed by humid forests near the ocean and semideciduous formations towards inland. This biome has only historical records of the Brazilian Merganser (Fig. 1), and only 12–28% of its original cover remains (Ribeiro et al., 2009; Rezende et al., 2018). The only ecoregion present in the Amazon is comprised by the Mato Grosso seasonal forests, located at the boundaries of the Amazon biome and included in geographic space because it is an ecotone with Cerrado characteristics. It is located in the Arc of Deforestation, a region of the Brazilian Amazon with the highest rates of deforestation (Matricardi et al., 2020).
Presence records and environmental predictorsWe compiled a presence-only database with 697 unique records from 2001 to 2019. The records were made by specialist researchers (FHP, FR, GMSD, LVL, MB, PTZA) during field activities using the active search method while walking along river margins, using boats along the river course (more information in Barbosa et al., 2015; Lamas, 2006; Lins et al., 2011), and by the small boat line-transect survey method (GMSD). We discarded records between 2001 and 2005 in areas where the species has not been recorded since then. The records were made at the Serra da Canastra region (n=491), Chapada dos Veadeiros (n=118), and Jalapão (n=88) (Fig. 1). We used the ‘Spatially Rarefy Occurrence Data for SDMs (reduce spatial correlation)’ tool from the SDMtoolbox package (Brown et al., 2017) in ArcGIS v. 10.2 (ESRI, 2014) to eliminate spatial dependence between presence records. We used different rarefaction distances following the information provided by the species experts about home-range sizes supported by extensive fieldwork, 5km for Jalapão (PTZA, MB), 10km for Chapada dos Veadeiros (GMSD, FHP), and 15km for Serra da Canastra (Silveira and Bartmann, 2001), resulting in 48 unique independent presence records for modeling. Most of the Brazilian Merganser's current records are located close to or within four strictly protected (IUCN Categories I–III; Dudley, 2008) PAs (Brazil, 2000): Serra da Canastra National Park (1980km2; Serra da Canastra region), Jalapão State Park and Serra Geral do Tocantins Ecological Station (1600 and 7160km2; Jalapão region), and Chapada dos Veadeiros National Park (2400km2; Chapada dos Veadeiros region).
We chose 30 environmental predictors, such as percentage of tree cover (Hansen et al., 2013), land cover classes (Projeto MapBiomas, 2019), topography (USGS, 2018), drainage (Rennó et al., 2008), and bioclimatic variables (Fick and Hijmans, 2017) (variable definitions and source available in Appendix 1). All these predictors were available in raster files, which were resampled to 1km of spatial resolution and limited according to geographic space boundaries to be used in Maxent. For modeling we only retained predictors not strongly correlated (Pearson's<0.7; Appendix 1).
Model buildingTo identify suitable areas for the Brazilian Merganser we used Maxent algorithm v.3.4.1 (Phillips et al., 2017a) in the Maxent software (Phillips et al., 2017b). We defined the following parameters for modeling: bootstrap method of replicates (n=10), 70% of the points to train and 30% to test, 10,000 background points, random seed, convergence threshold of 10−5, 500 maximum iterations and cloglog output format. We cut the model using the maximum testing sensitivity plus specificity cloglog threshold (0.124), resulting in a binary map (0=unsuitable; 1=suitable). Since the Brazilian Merganser is associated to river courses, we cut the final model by a mask of 1km buffer from the hydrological network available in IBGE (1:250,000; IBGE, 2017), assuming unsuitability of areas outside this mask. Due to the high resolution of the hydrological network, we only considered named water bodies, excluding seasonal or very small streams that would lack the Brazilian Merganser's requirements.
Model evaluationWe evaluated the model using AUC (area under the curve – ROC) (Fielding and Bell, 1997; Lobo et al., 2008). The ROC is built using sensitivity (capacity to correctly predict true presences) and specificity (capacity to correctly predict areas without records as unsuitable) values (Jiménez-Valverde, 2012). AUC values around 0.5 are not better than a random model, above 0.7 are acceptable, and higher than 0.9 are very good (Peterson et al., 2011). Apart from the statistical performance, we selected the final model only after a common agreement among all experts at the BMNAP meeting in March 2020, following the Participatory Modeling Process (Ferraz et al., 2020). We overlapped the final model in the MapBiomas land cover map (30m) to characterize the Brazilian Merganser's suitable areas in the entire geographic space.
Suitable areas analysisTo restrict our analysis of SHP's potential impact and PAs coverage over suitable areas, we created a buffer with the maximum dispersion distance for the species (20km; Ribeiro et al., 2011) as a radius around presence records (hereafter dispersion zone). To evaluate the potential impact of the SHPs over the potential species distribution we created a buffer of 3km radius around each SHP (hereafter ‘impact zone’). We chose this distance based on the maps of 10 SHP reservoirs present in the Brazilian Cerrado (D’Arc, 2018). The average linear distance from the SHP dam to the most distant point of the reservoir was higher than 4km, so we used 3km to be conservative. Then, we overlapped the SHP impact zone and the dispersion zone to calculate the likely proportion of suitable area impacted by SHPs. We considered separately those already operating and those planned but not yet built. The existing and planned SHP database was downloaded from the official Brazilian electric energy agency website (ANEEL, 2020). We also calculated the suitable area for the Brazilian Merganser inside PAs (strict protection status, according to the Brazilian legislation; Brasil, 2000), as well as the amount of each land cover category within the suitable dispersion zone.
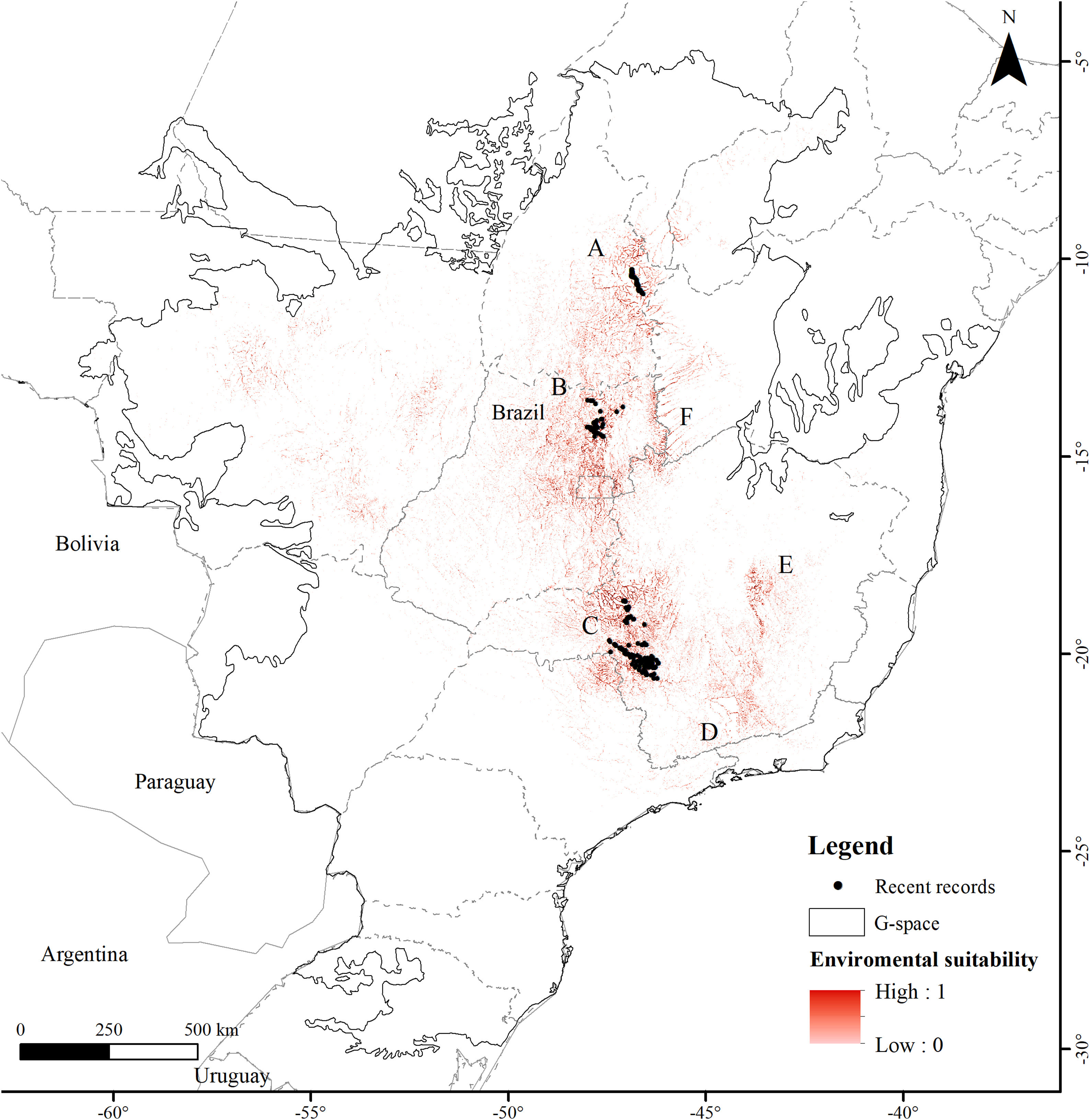
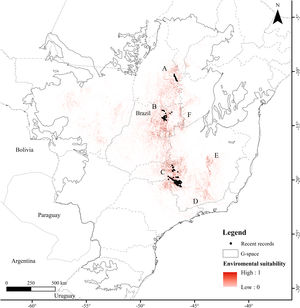
ResultsThe Brazilian Merganser's potential distribution model presented a high performance (AUC=0.968±0.012, omission=0.021 and p-value=0.05; Fig. 2) and predicted only ~4% of the geographic space as suitable for the species (142,899km2). The final model identified the three regions with confirmed presence as suitable for the species (Serra da Canastra, Chapada dos Veadeiros and Jalapão). Three additional regions lacking recent records of the species were identified as suitable (Serra do Espinhaço, Serra da Mantiqueira and Grande Sertão Veredas region; Fig. 2). The most important variables explaining the species distribution were land cover (17.26%), precipitation of coldest quarter (Bio 19, 15.22%), flow accumulation (11.78%), Vector Ruggedness Measure (8.93%), and elevation (DEM, 8.5%) (Appendix 2). The dominant land uses surrounding rivers in the suitable area were pasture (20.96%, 29,950km2), forests (20.84%, 29,781km2), savannas (20.81%, 29,742km2), and grasslands (15.28%, 21,835km2) (Appendix 3).
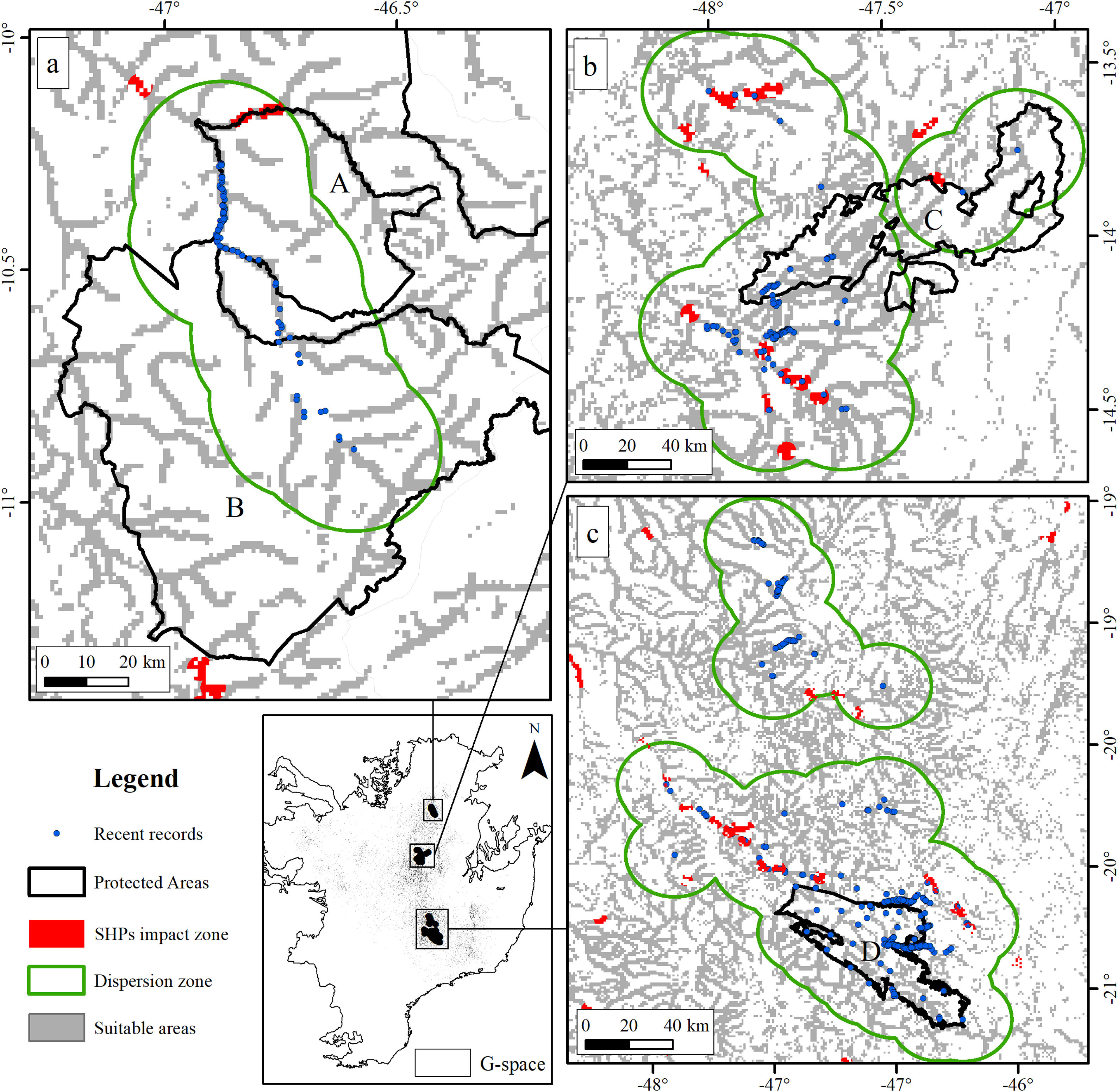
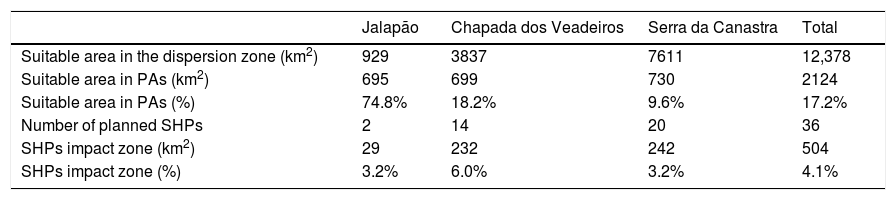
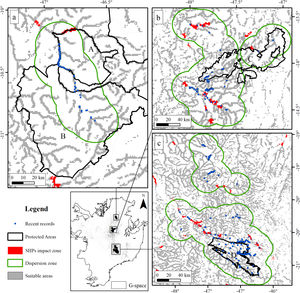
The suitable area for each region considering only the dispersion zone was 930km2 for Jalapão, 3837km2 for Chapada dos Veadeiros and 7611km2 for Serra da Canastra, totalizing 12,378km2 (Table 1; Fig. 3). There is no SHP in operation within the dispersion zone, but 36 are planned to be built in the coming years, which could impact 504km2 of the Brazilian Merganser's suitable area, i.e., 4.1% of the suitable area within the species’ potential dispersion zone. If those planned SHPs are built, the most affected region will be Serra da Canastra, with 20 planned SHPs and 242km2 of impacted area in the species’ suitable area (Fig. 3b). Chapada dos Veadeiros and Jalapão have 14 and 2 planned SHPs each, which can respectively impact 232km2 and 29km2 of the total suitable area in the dispersion zone (Fig. 3a and c). The total amount of suitable area in PAs is 2124km2, 17.2% of the suitable area in the total dispersion zone. The percentage of the suitable area of the dispersion zone within PAs is 9.6% in Serra da Canastra, 18.2% in Chapada dos Veadeiros, and 74.8% in Jalapão (Table 1). The predominant land covers in the dispersion zone are grassland (28.03%, 3346km2), forest (15.51%, 2210km2), pasture (16.76%, 2000km2) and savanna (15.70%, 1874km2) (Appendix 3).
Suitable area, Protected Areas (PAs) and number of planned small hydroelectric plants (SHPs) inside the dispersion and impacted zones of the three Brazilian Merganser populations.
| Jalapão | Chapada dos Veadeiros | Serra da Canastra | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Suitable area in the dispersion zone (km2) | 929 | 3837 | 7611 | 12,378 |
| Suitable area in PAs (km2) | 695 | 699 | 730 | 2124 |
| Suitable area in PAs (%) | 74.8% | 18.2% | 9.6% | 17.2% |
| Number of planned SHPs | 2 | 14 | 20 | 36 |
| SHPs impact zone (km2) | 29 | 232 | 242 | 504 |
| SHPs impact zone (%) | 3.2% | 6.0% | 3.2% | 4.1% |
The three remaining regions with confirmed presence of Brazilian Merganser (a: Jalapão; b: Chapada dos Veadeiros, and c: Serra da Canastra) and the suitable, protected, dispersion, and SHP impacted areas. Capital letters indicate Protected Areas: A: Jalapão State Park; B: Serra Geral do Tocantins Ecological Station; C: Chapada dos Veadeiros National Park, and D: Serra da Canastra National Park.
Our modeling approach revealed the scarcity of suitable areas for the remaining populations of the Brazilian Merganser. Although the regions with recent records presented high suitability, several areas where the species occurred in the past are currently unsuitable. Conversely, our model also pointed out suitable areas without recent records of the Brazilian Merganser, which we urge to be targeted in near future expeditions looking for this species. Grande Sertão Veredas lacks any records since 1999 (Pineschi and Yamashita, 1999) and the last sighting in the corridor that links Serra da Mantiqueira to Serra do Espinhaço dates back to 2004 (Paula et al., 2008).
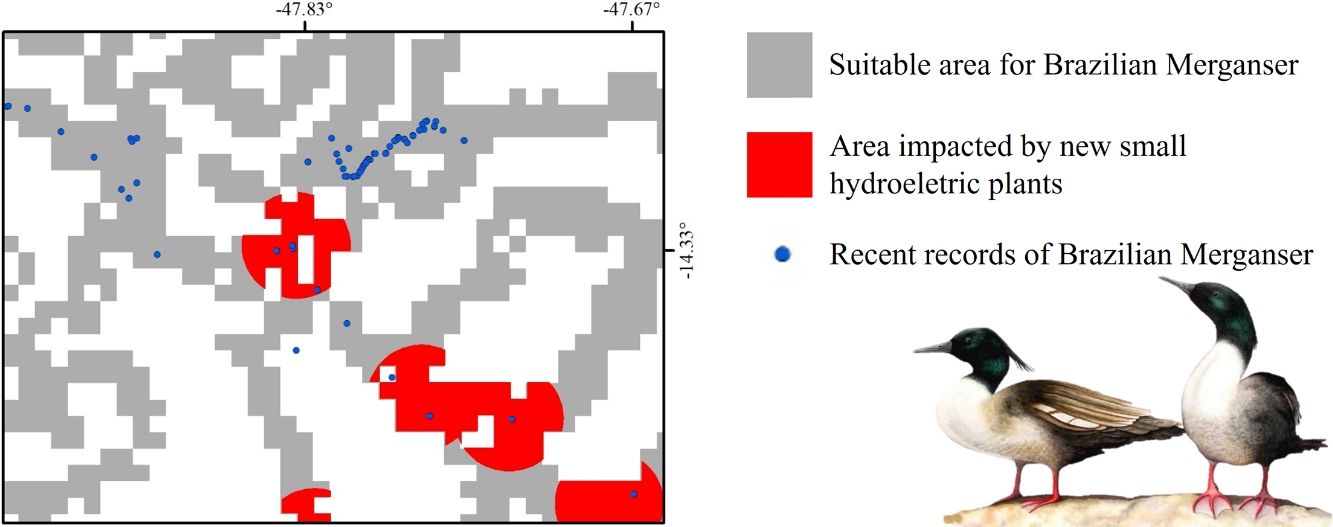
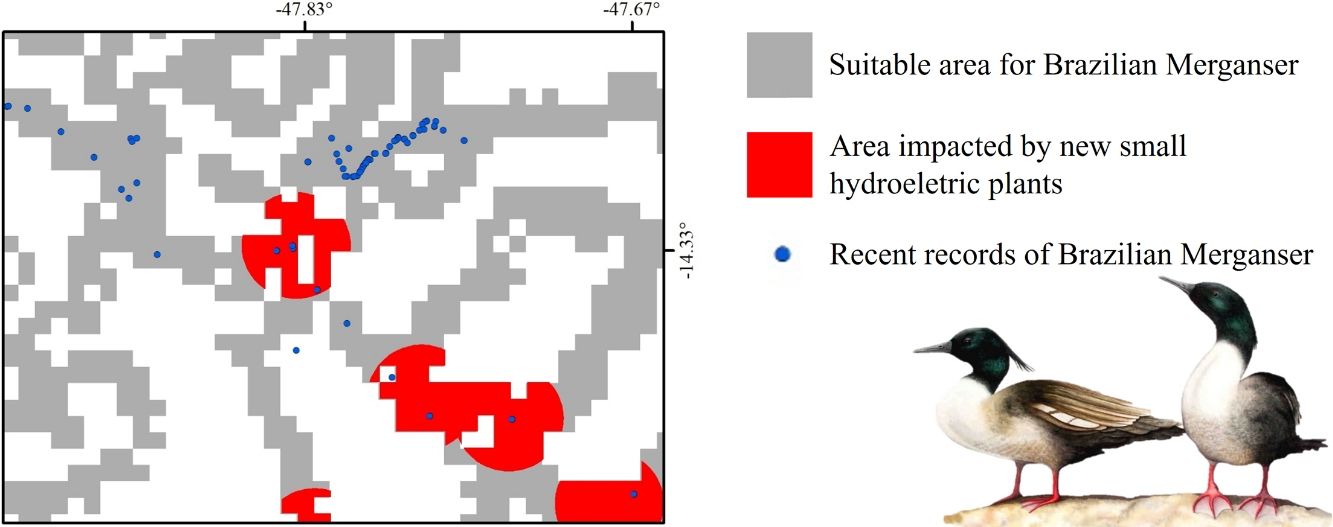
Small hydroelectric plantsOur analysis revealed the likely heavy impact on the Brazilian Merganser's suitable areas if the construction of the 36 planned SHPs on rivers inhabited by the species begin in the coming years. The potential impact predicted on the Brazilian Merganser by SHP construction should not be ignored as it affects every known remaining population. Even in Jalapão, where the impact is predicted to be smaller, the loss of the few remaining suitable areas can be too harsh for such a small population that already suffers other major threats (e.g. rafting in the reproductive season; Barbosa et al., 2015). The high number of SHPs planned to be built at Serra da Canastra highlights the importance of urgent conservation actions in this region, which harbors more than half of the Brazilian Merganser's population (Ribeiro et al., 2018). Araguari river basin holds the largest number of individuals in Serra da Canastra and outside PAs and has 11 planned SHPs that could put in risk 18% of the global population. The implementation of new SHPs may disrupt the natural connection of rivers in the Chapada dos Veadeiros region, especially in the southern, central and northern parts (sub-basin of the Tocantinzinho, Preto, Almas, and São Félix rivers), which may impact the movement and dispersion of species, compromising the maintenance of biodiversity in Chapada dos Veadeiros National Park (Disconzi, 2012). The largest number of planned SHPs in Chapada dos Veadeiros are in the south, especially in the Tocantinzinho river, which has the greatest concentration of species territories in the region.
Habitat loss caused by dams have already been reported in Brazil (Serra da Canastra; Lamas, 2006), Argentina and Paraguay, after the construction of the Itaipu, Acaray and Yacyreta dams, respectively (Hughes et al., 2006). For instance, the construction of Urugua-í dam in Argentina can be the cause of the Brazilian Merganser's local extinction in that region (Johnson and Chebez, 1985). Although the impact of a single SHP is much smaller than that of a conventional hydroelectric plant, it causes enough changes in river flow to affect this sensitive species. The shift of a lotic to lentic ecosystem after a dam flooding eliminates the ecological requirements of the Brazilian Merganser (e.g. clean and rapid water; Hughes et al., 2006), an anthropogenic environmental change that has impacted or threatened many other species worldwide (Reitan and Thingstad, 1999; Laurance et al., 2020). The predictable and unavoidable changes in rivers caused by dams will reduce the availability of new territories for young dispersing Brazilian Merganser. In a scenario of insufficient rapids and streams with clear water, it is unlikely that these individuals will be able to establish their own territories, which would ultimately increase the risk of extinction on a regional scale due to reduced recruitment in a given population.
We must stress the SHP impacts (Premalatha et al., 2014), but also the importance and potential of this energy source (Ferreira et al., 2016). Our results show how SHPs can negatively affect a critically endangered species, and we urge that environmental impact assessments consider it when analyzing the viability of new SHP projects. In cases where the Brazilian Merganser would potentially be affected, SHP project relocation or alternative energy sources should be considered. Instead of advocating against SHPs, we are adding a piece of information to better balance pros and cons in the decision-making process.
Anthropogenic land use and protected areasIn addition to SHP threats, anthropogenic land use surrounding currently known habitats of the Brazilian Merganser and the low amount of suitable strictly protected areas for this species reveal its critical situation. This scenario emphasizes the importance of valuing efforts to evaluate and minimize known threats to this species when planning for the Brazilian Merganser's conservation. Although natural land cover predominates in the suitable areas (~60% of forest, savanna and grassland), the presence of pasture and agriculture in those areas (36.6%) and within the dispersion zone (32.8%) is worrying, especially given the importance of the land cover in explaining the Brazilian Merganser's distribution. A series of indirect impacts can be carried-on to the streams where the surrounding areas are not covered by natural vegetation.
The intensification of agriculture activities in the Cerrado in the last decades directly affects the species through habitat conversion and impacts on water quality (Hunke et al., 2015), and decreases river flow due to the use of water for cropland irrigation (Latrubesse et al., 2019). Other factors promote river siltation following erosion, such as poorly planned roads, and mining (Bruno, 2004; Hughes et al., 2006). Those activities can increase water turbidity, which is avoided by the species (Silveira and Bartmann, 2001). Siltation can offer harsh consequences, being pointed out as the main reason for population decline in Argentina (Hearn, 1994). Other human threats are also relevant for the species’ conservation and should be considered, such as industrial and urban pollution, criminal fires (Hughes et al., 2006; Lamas, 2006), the massive presence of tourism in waterfalls and along watercourses, and unregulated rafting and canoeing (Silveira and Bartmann, 2001).
These impacts highlight the importance of natural land cover to the conservation of the Brazilian Merganser and the role of PAs, which maintain the native vegetation and avoid, at least partially, impacts on water quality. All the regions with recent records of the Brazilian Merganser are near PAs, but less than one-fifth of the suitable areas in the dispersion zone are legally protected. Jalapão has the highest percentage of suitable area in PAs, but most of the presence records of the species are located in the Jalapão State Park surroundings (Barbosa et al., 2015), and only less frequently inside the Serra Geral do Tocantins Ecological Station. Outside PAs, the suitable areas for the Brazilian Merganser are composed by a mosaic of natural and anthropogenic land use areas, the latter scenario known to often promote degradation of water quality in catchment areas (Latrubesse et al., 2019). A similar situation occurs in Serra da Canastra, where less than 20% of the individuals are protected by the National Park, the remaining being subject to several anthropogenic impacts.
Final considerationsThe Brazilian Merganser is a critically endangered species, and its three known remaining populations could be severely affected by the construction of new SHPs, including the ones already planned. The impact on such an endangered species should be weighed and balanced against SHP benefits, and alternatives should be considered to avoid or mitigate impacts. We acknowledge that field validation of our SDM is a mandatory next step for this study, but our findings are an important asset for planning ongoing searches for new Brazilian Merganser populations and for revisiting areas with recent records (i.e., last 30 years) that lack further follow-up studies. The high environmental suitability of the northern portion of Serra do Espinhaço suggests that it must be evaluated as a high priority area to search for new populations of the Brazilian Merganser in the coming years. As research funds are limited and prospective areas for the species are scattered, the model is therefore a useful tool to guide the allocation of necessary resources. In a world of fast conversion of natural habitats for human use, identifying highly suitable areas for the Brazilian Merganser and understanding how this species can be negatively affected by human development is paramount for guiding its conservation. The Brazilian Merganser is naturally rare and has already suffered a huge contraction of its original distribution over the last century. By detailing how critical the situation is for the species, our results and findings thus urge for conservation actions. Every effort counts for protecting the remaining populations of the Brazilian Merganser and for increasing the occupation of suitable regions by this species in the near future.
FundingThis work was financed in part by the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior – Brasil (CAPES) – Finance Code 001; the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq) for the productivity fellowship to KMPMBF (process 308632/2018-4) and LFS (process 308337/2019-0); and the CAPES for the post-doc fellowship to ACG (88882.306082/2018-01).
We thank the ICMBio, IUCN SSC CPSG, Parque das Aves and Zooparque for supportting the Conservation Action Plan Workshop. We also thank Flávio K. Ubaid, Leticia Pereira Silva, Rita C.S. Medeiros, Fabrizio Pereira, Chapada dos Veadeiros National Park/ICMBio, CEPF/IIEB for supporting the research activities at Chapada dos Veadeiros (Goiás).