The Impact Factor measures the average number of citations received in a particular year by papers published in the journal during the two preceding years.
© Clarivate Analytics, Journal Citation Reports 2025
- •
Endemics–area relationships (EARs) are largely lacking for plants.
- •
Our new EAR method overcomes key biases to model expected numbers of plant endemics.
- •
Our global model for vascular plants is Endemics=0.00001227·Area1.195 (area in km2).
- •
The model gives baseline endemism for circular areas in the range 104–108km2E=0.0000127·A1.195.
- •
The average area needed for at least one endemic vascular plant species as 12,875km2.

- •
Spatial richness patterns will be maintained in the future but with a general loss in species number.
- •
Spatial beta diversity will increase in the future, enhancing the spatial heterogeneity.
- •
Beta diversity will change through time.
- •
Changes in spatial and temporal beta diversity are mainly in turnover and nestedness, respectively.
- •
Beta diversity changes may be due to reductions in primates distributions.

- •
Niche modelling and Alpha and Beta diversity analyses in Brazilian Cerrado.
- •
Biotic homogenization in Southern Cerrado.
- •
Species richness loss throughout Cerrado.

- •
None of the covariates tested influenced the occupancy probability of the cattle.
- •
The occupancy of donkey was influenced positively by the distance from the nearest ranch.
- •
The habitat type influenced the detection of species.
- •
The probability of detection of herbivores was higher in the shrubby-arboreal Caatinga.

- •
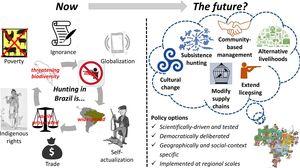
Hunting is banned in Brazil.
- •
Illegal hunting in Brazil is widespread and cultural embedded.
- •
Data about wildlife, habitat distribution and motivations for hunting are lacking.
- •
Main factors driving non-compliance are analyzed and discussed.
- •
Policy options to deal with hunting in the future are proposed.
- •
Inadequate application of the CONAMA resolution 423/2010 threatens conservation in campo rupestre (CR).
- •
The list of bioindicator species currently used comprises only 2.9% of the known flora of the CR.
- •
There is no scientific basis to support sere classification in CR.
- •
CR is in a retrogressive phase of ecological succession.
- •
Revising and creating specific legislation to protect the CR is pressing.







