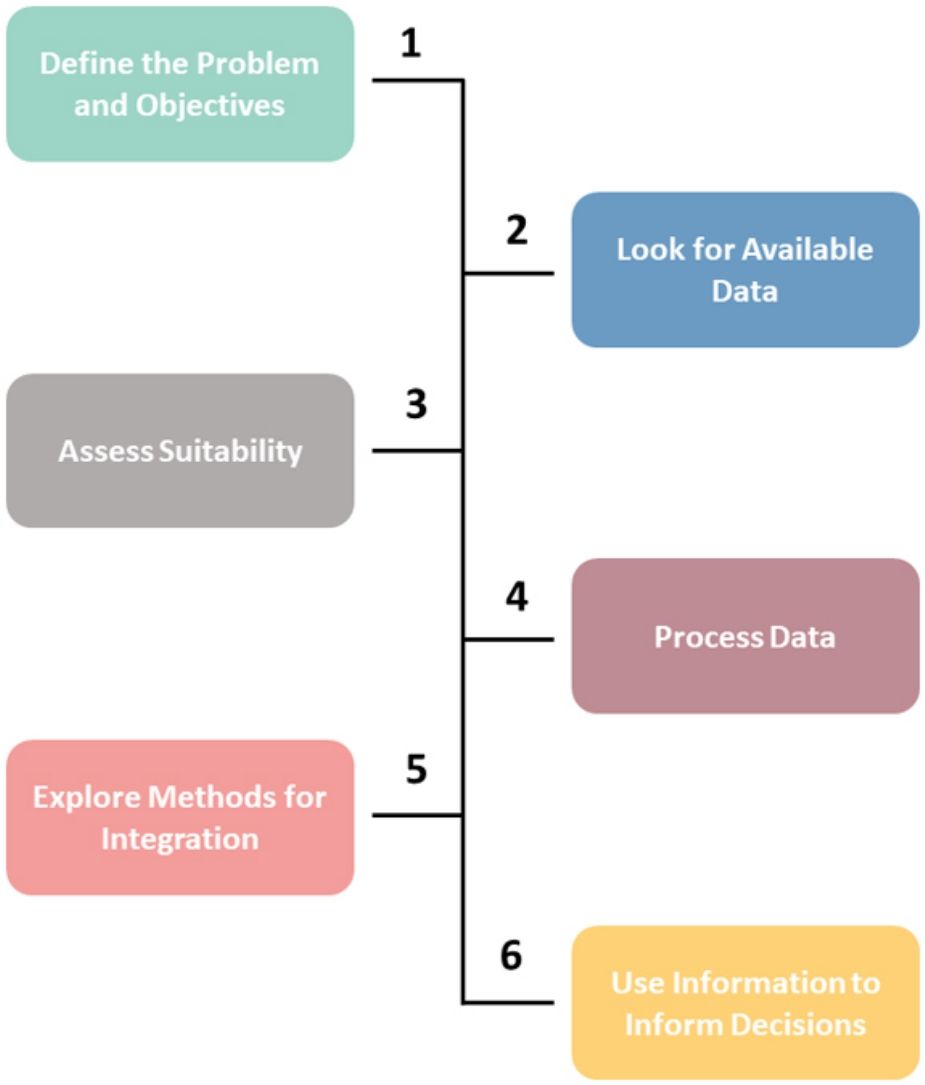
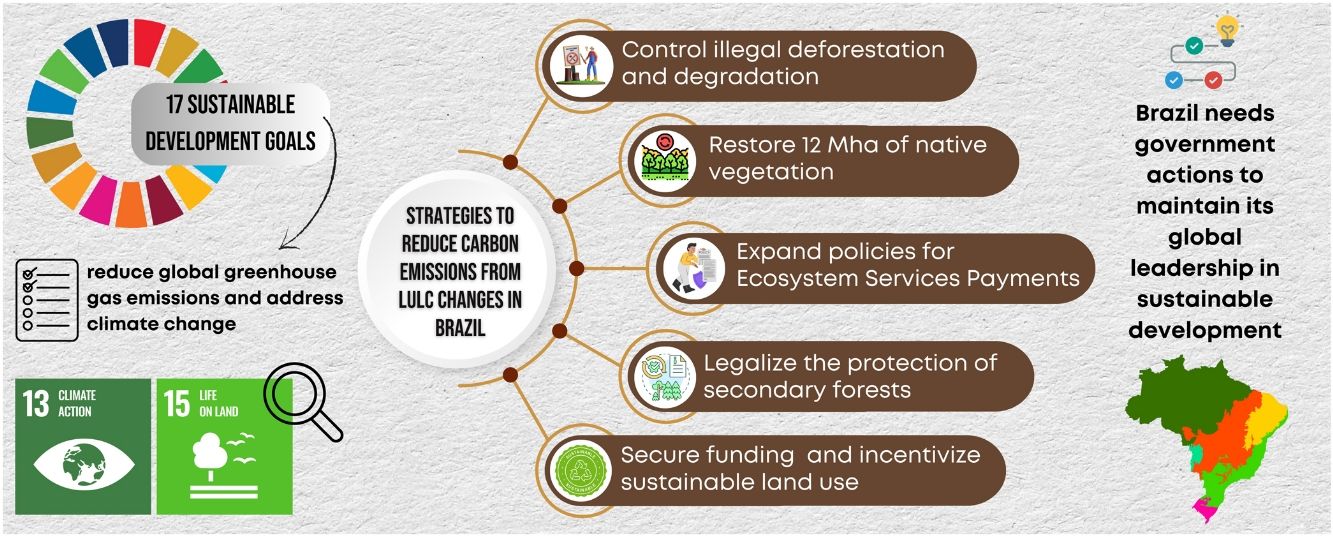
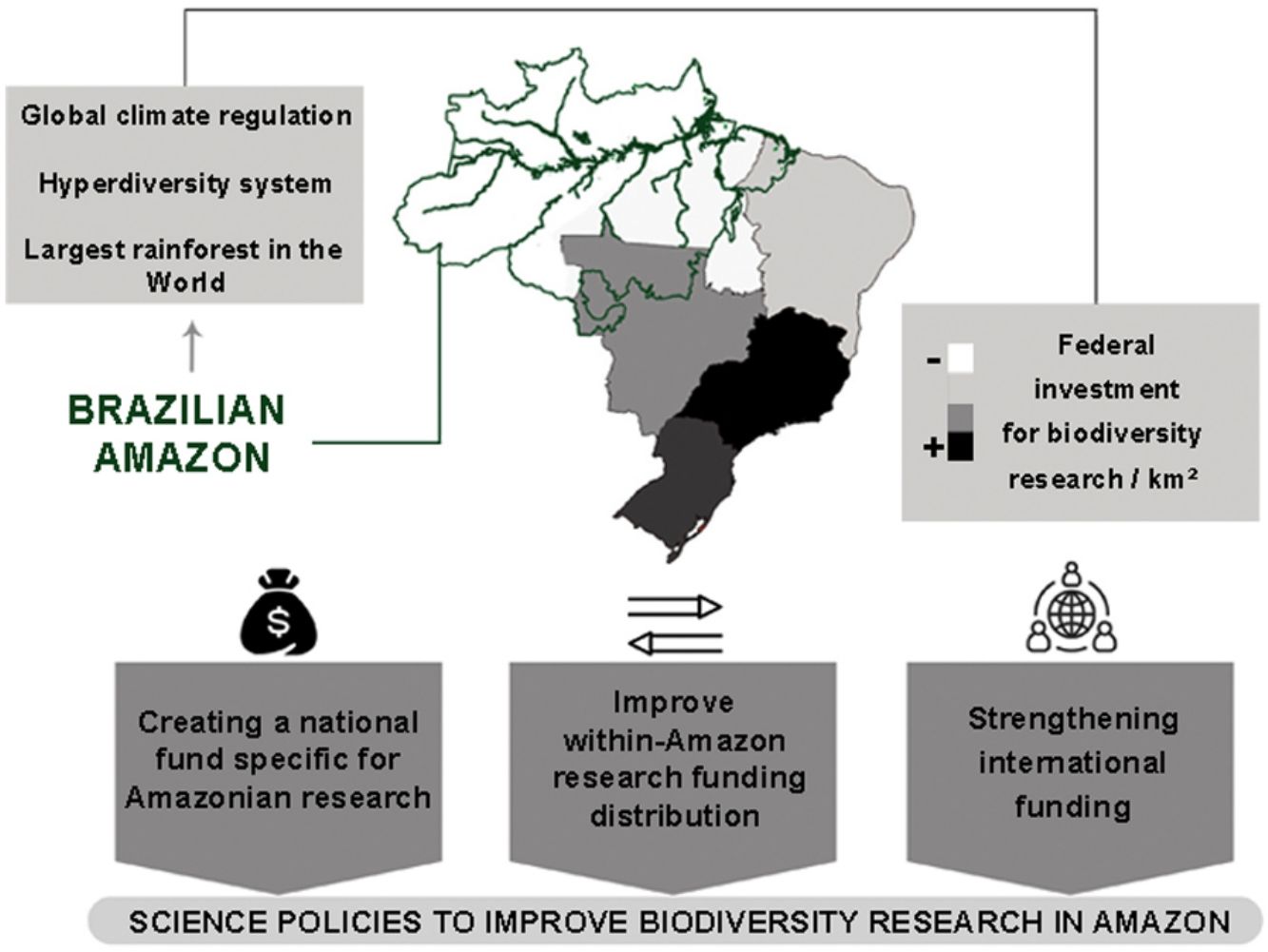
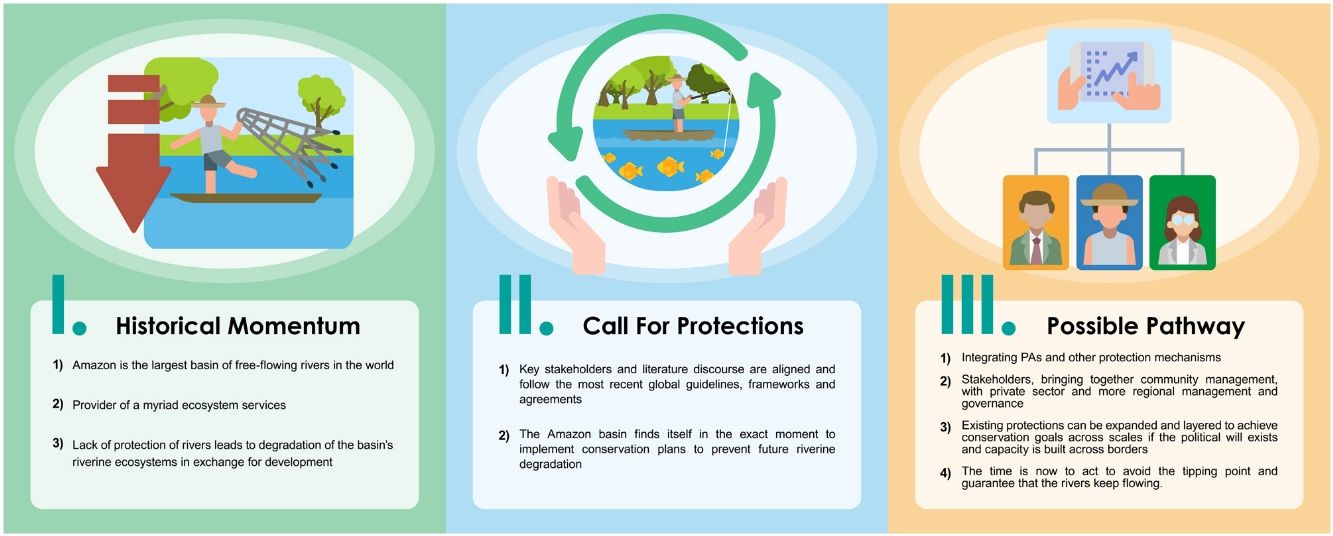
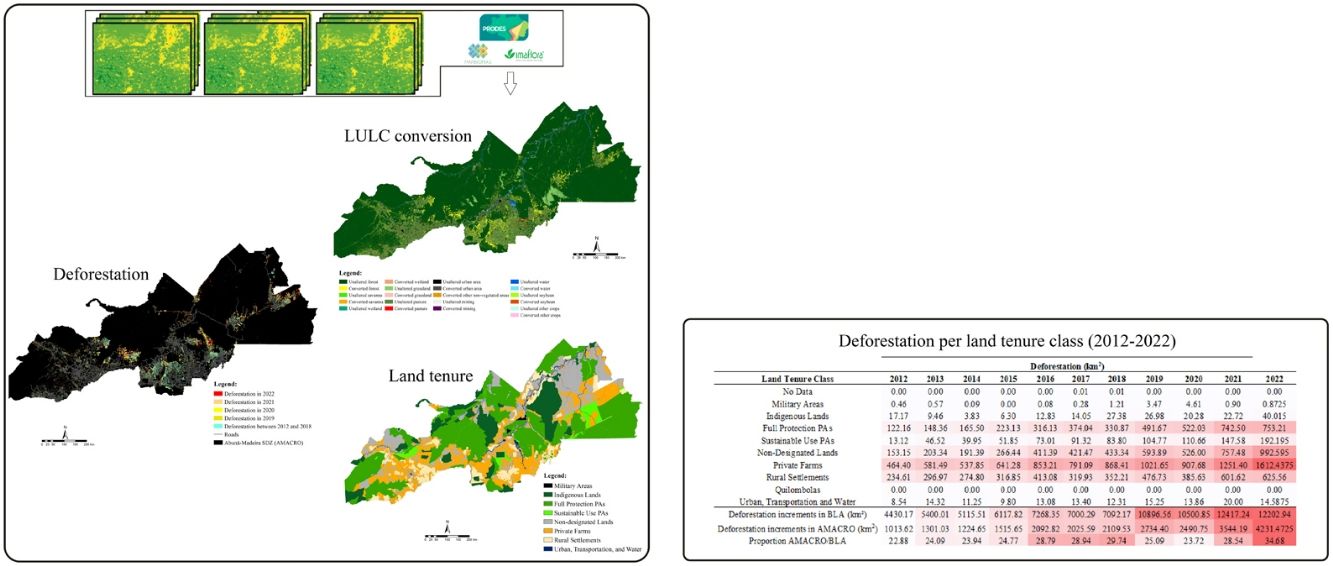
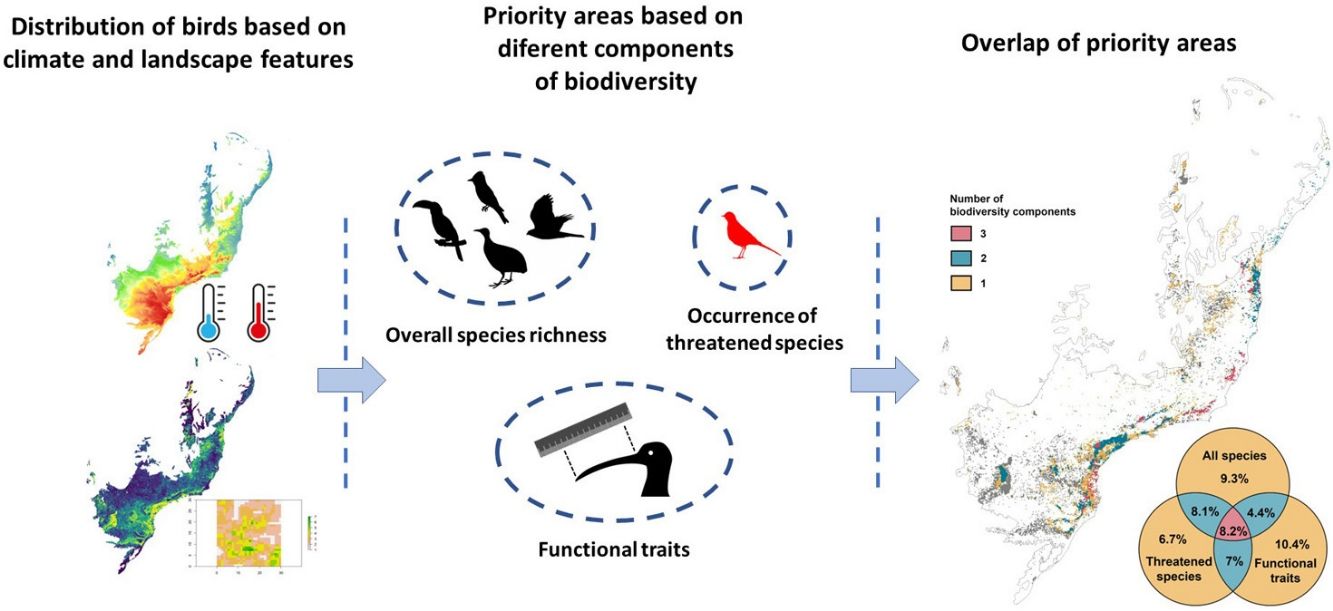
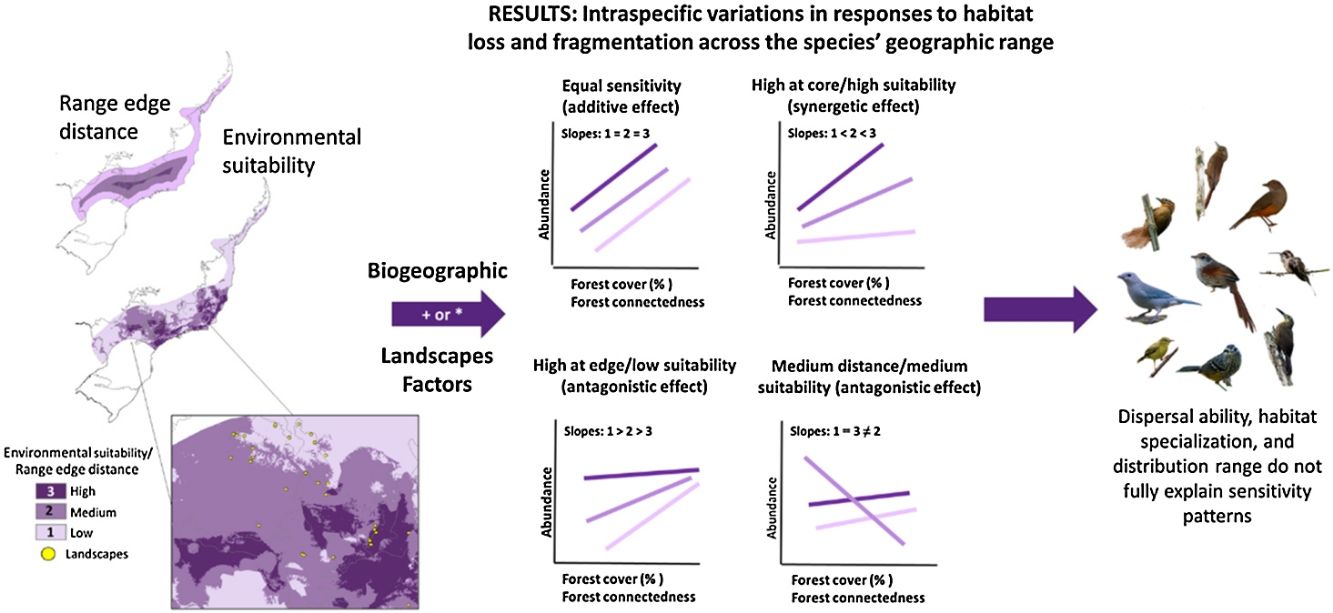
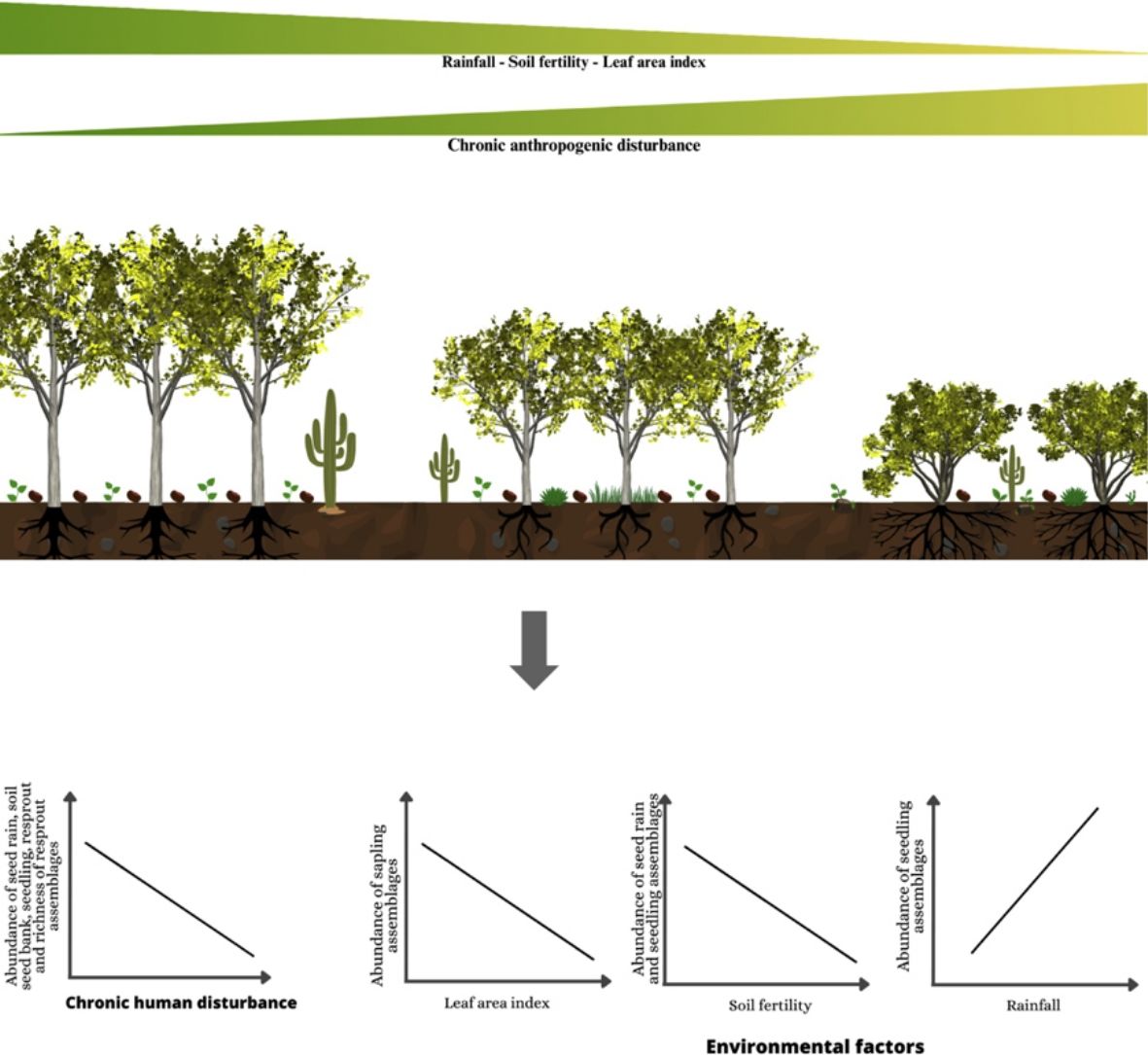
Perspectives in Ecology and Conservation (PECON) is a scientific journal devoted to improving theoretical and conceptual aspects of conservation science. It has the main purpose of communicating new research and advances to different actors of society, including researchers, conservationists, practitioners, and policymakers. Perspectives in Ecology and Conservation publishes original papers on biodiversity conservation and restoration, on the main drivers affecting native ecosystems, and on nature¿s benefits to people and human wellbeing. This scope includes studies on biodiversity patterns, the effects of habitat loss, fragmentation, biological invasion and climate change on biodiversity, conservation genetics, spatial conservation planning, ecosystem management, ecosystem services, sustainability and resilience of socio-ecological systems, conservation policy, among others.
Perspectives in Ecology and Conservation is the official scientific journal of the Brazilian Association for Ecological Science and Conservation. It is an open access journal, supported by the Boticário Group Foundation for Nature Protection, and thus without any charge for authors. Perspectives in Ecology and Conservation was previously published, between 2003 and 2016, as 'Natureza & Conservação'.